It does not have any cycles (circuits, or closed paths), which would imply the existence of more than one path among two nodes. It is the most general kind of tree, and might be converted in the more familiar form though designating a node as the root. We can represent a tree like a construction containing nodes, and edges that represent a relationship among two nodes. In Figure, we will assume most common tree called rooted tree. A rooted tress has a single root node that has no parents.
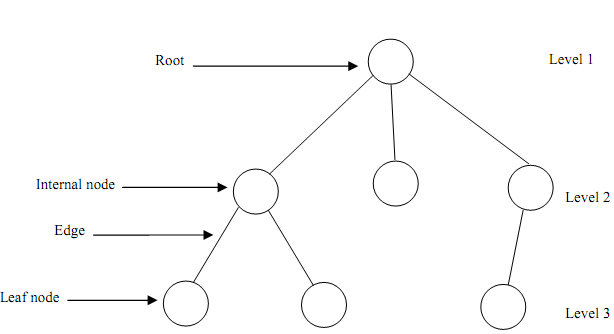
Figure: A rooted tree
In more formal way, we can define tree T like a finite set of one or more nodes such that there is one designated node r called as the root of T, and the remaining nodes into (T - { r } ) are partitioned in n > 0 disjoint subsets T1, T2, ..., Tk each of is a tree, and whose roots r1 , r2 , ..., rk , respectively, are children of r. The general tree is a generic tree which has one root node, and each node in the tree can have limitless number of child nodes. One popular employ of this kind of tree is a Family Tree.
A tree is an example of a more general category called graph.
- A tree contains nodes connected by edges.
- A root is node without parent.
- Leaves are nodes having no children.
- The root is at level 1. The child nodes of root are at level 2. The child nodes of nodes at level 2 are at level 3 and so forth.
- The depth (height) of any Binary tree is equivalent to the number of levels in it.
- Branching factor describe the maximum number of children to any node. Thus, a branching factor of 2 means a binary tree.
- Breadth described the number of nodes at a level.
- In a tree the depth of a node M is the length of the path from the root of the tree to M.
- In a Binary tree a node has at most 2 children. The given are the properties of a Tree.
Full Tree: A tree having all the leaves at the similar level, and all the non-leaves having the similar degree
- Level h of a full tree contains dh-1 nodes.
- The first h levels of full tree have 1 + d + d2 + d3 + d4 + ....... + dh-1 = (dh -1)/(d - 1) nodes where d refer to the degree of nodes.
- The number of edges = the number of nodes - 1 (Why? Because, an edge represents the relationship among a child & a parent, and every node has a parent except the root.
- A tree of height h & degree d has at most d h - 1 element.