Risk Identification
Risk management comprises of identifying, classifying and prioritizing organization’s information assets, threats and vulnerabilities also. Risk Identification ascertains which kinds of risks have the potential of affecting the project and documenting risks’ characteristics. Risk Identification begins after Risk Management Plan is constructed and continues throughout the project execution. The Risk Identification procedure naturally progresses into the Qualitative Risk Analysis or Quantitative Risk Analysis Process. At times it is wise to include the identification of a risk and its response in order for it to be included in Risk Response Planning.
At the starting of the Risk Identification process it is a good to have gathered all of the inputs you and your team will require. The inputs to Risk Identification Process
are:
•The Project Management Plan - It is used in gain an understanding of the project’s mission, schedule, scope, cost, Work Breakdown Structure (WBS), quality criteria, and some other elements.
•Risk Management Plan - It provides the blueprint of overseeing risk management throughout project describing who, when, where, why, what, and how. It provides the following four critical inputs to Risk Identification:
oAssignment of roles and responsibilities – by identifying the who of risk management and by assigning the handling of specific tasks and roles to particular individuals.
o Budget provisions for risk-management activities - The approved funds which are available for risk management activities. You will require tracking your actual costs against these approved budget numbers.
o Schedule for risk management - The revised schedule including the time required for risk management activities over duration of the project’s life cycle.
o Categories of risk - The risk categories are used at the time of Risk Identification to organize and prioritize risks as they are identified. On the other hand, the Risk Breakdown Structure (RBS) can be the source of risk categories.
•Project Scope Statement - The project scope statement defines the project assumptions and boundaries. During Risk Identification, risks to boundaries should be identified in order to mitigate scope creep, and assumptions should be reassessed to identify risks connected with them.
•Organizational process assets - Organizational process assets give information from prior projects including historical information and lessons which are learned.
•Enterprise environmental factors - These factors include all external environmental factors and internal organizational environmental factors which surround or influence the project’s success, such as organizational culture and structure, market conditions, existing resources, infrastructure, commercial databases, and project management software.After gathering all the essential inputs, it is time to employ the advised tools and techniques of risk identification. The tools and techniques are:
oDocumentation reviews – It involve comprehensively reviewing the project documents and assumptions from project overview and detailed scope perspective in order to identify areas of inconsistency or less of clarity. Missing information and inconsistencies are indicators of risks which are hidden.
oInformation gathering techniques – These are used to develop lists of risks and risk characteristics. Each technique is useful for collecting a particular kind of information. The 5 techniques are:
oBrainstorming - Brainstorm is used as a general data gathering and creativity technique which identifies ideas, risks, or solutions to issues. Brainstorming makes use of a group of team members or subject matter experts spring boarding off each others’ ideas, to generate the new ideas.
oDelphi technique - The Delphi technique takes information from expert, about the likelihood of future events occurring. The technique eliminates bias and prevents any one expert from having influence on the others.
oInterviewing - Interviewing in meeting comprised of project participants, subject-matter experts, stakeholders, and individuals who may have participated in past projects is a technique for gaining 1st hand information about and benefit of others’ knowledge and experience.
oRoot cause identification - Root cause identification is a technique for identifying necessary causes of risk. By using data from an actual risk event, the technique enables you to find what occurred and how it occurred, and understand why it occurred, so that you can devise responses to prevent from the recurrences.
oStrengths, opportunities, weaknesses, and threats (SWOT) analysis - A SWOT analysis examines project from the perspective of each project’s strengths, opportunities, weaknesses, and threats to increase the breadth of risks considered by risk management.
oChecklist analysis - It list all identified or potential risks in a place.These are commonly developed from historical information. The Risk Breakdown Structure (RBS) can be used as a checklist. Keep in mind that checklists are never comprehensive, so using another technique is still required.
oAssumptions analysis - All the projects are initially planned on a set of assumptions and what if scenarios. These assumptions can be documented in Project Scope Document. At the time of Risk Identification, assumptions are analyzed to determine amount of inconsistency, inaccuracy, or incompleteness which is associated with them.
oDiagramming techniques - Diagramming techniques, such as system flow charts, cause and effect diagrams, and influence figures are used to uncover risks that are not readily apparent in verbal descriptions.
o Cause and effect diagrams – This figures or fishbone diagrams are used for identifying causes of risk
oSystem or process flow charts - Flow charts illustrate how elements and processes interrelate.
oInfluence diagrams - Influence figures depict causal influences, time ordering of events and other relationships between input and output variables.
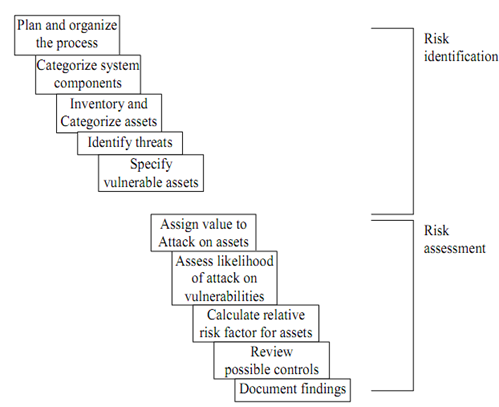
Risk identification starts with identifying organization’s assets and assessing their value as shown in the Figure given below