Residential Access
Residential access is connecting home end systems ( typically a PC but increasingly a home network) into the network. One form of residential access is the dial up modern over an ordinary analog telephone line into a residential ISP ( Internet Service Provider). The home modern converts the digital output of the PC into analog format for transmission over the analog phone line. This analog phone line is made of twisted pair copper wire and is the same telephone line sued to make ordinary phone calls. At the other end of the analog phone line a modern in the internet serves provider(ISP) convert the analog signal back into digital form for input to the ISP router. Thus the access network is simply a pair of modems analog with a point to point dial up phone line.
Today modern speeds allow dial up access at rates upto 56kbps. However due to the poor quality of the twisted pair time line between many homes and ISP many users get an effective rate significantly less than 56 5bps. Moreover while a residential user uses a dial up modern to surf the web the user cannot receive and make ordinary phone calls over the phone line. Fortunately new broadband access technologies are providing residential users higher bit rates and they are also providing a means for users to access the internet and talk on the phone at the same time. There are two common types of broadband residential access.
1.Digital subscriber line (DSL)
2.Hybrid Fiber Coaxial Cable(HFC)
DSL access is typically by a telephone company. Sometimes in partnership with an independent ISP. Similar to dial up modems. DSL is a new modem technology again running over existing twisted pair telephone lines. But by restricting the distance between rates are typically asymmetrical into directions with a higher rate from ISP router to home than form the home to ISP router.DSL can provide bit rates more than 10 Mbps from ISP to home and more than 1 Mbps form home to ISP.
DSL divides the communication link between the home and the ISP into three non overlapping frequency bands.
3. A high speed downstream channel in th e50KJs to | MHz band
4.A medium speed upstream channel in the 4 KHz to 50 KHz band
5. An ordinary two way telephone channel in the 0 to 4 KHz band
While DSL and dial modems use ordinary phone lines. HFC access networks are extensions of the current cable network used for broadcasting cable television. In a traditional cable systems a cable head end broadcasts through a distribution network of coaxial cable and amplifiers to residence. As illustrated in figure 2.4 fiber optics connect the cable head end to neighbourhood level junctions from which traditional coaxial cable is then used to reach individual houses and apartments. Each neighbourhood junction typically supports 500 to 5000 homes.
DSL HFC requires special modems called cable modems typically the cable modern is an external device and connects to the home Pc through a 10 Base T Ethernet port. As with DSL the downstream channel is typically allocated more transmission rate than the upstream channel.
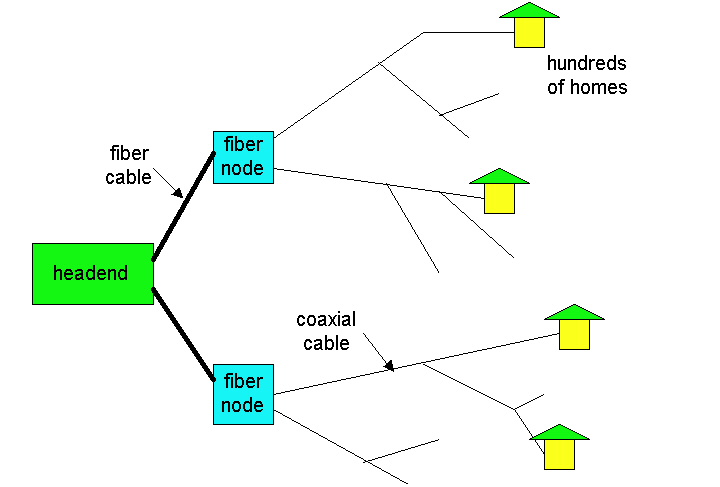
figure A Hybrid Fiber Coaxial Access Network
One important characteristics of GFC is that it is a shared broadcast medium. In particular every packet sent by the head end travels downstream to every link to every home and every packet sent by a travels through the upstream channel to the head end.
One of the attractive features of DSL and HFC is that user will by stay connected to the ISP while simultaneously making and receiving ordinary telephone calls.