Reproduction
Living things do not arise spontaneously. They arise only from pre-existing living things This is one of the fundamental tenets of biology. The ability of an organism to reproduce its kind is characteristic of living things. Reproduction involves transmission of information by the remarkable hereditary material deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) contained in the nucleus. The heredity material is subject to change or mutation. When provided with necessary conditions the DNA molecule is capable of replicating itself. The DNA codes for the information regarding structure and function of the organisms.
For example, DNA ensures that cats always produce kittens, never pups. In simple organisms such as protists, reproduction may be asexual. For example, a protist like amoeba reproduces by simple division. When the amoeba grows to a certain size it makes a duplicate copy of its DNA, each copy separating into a nucleus. The amoeba divides into two, each daughter amoeba thus possessing a nucleus with a copy of DNA. However, higher plants and animals reproduce sexually. This involves the union of a male gamete and female gamete. The male gamete is the sperm whereas the female gamete is the egg.
The sperm fertilizes the egg to form a zygote which then develops into a new individual. Each gamete has ope complete copy of genes (DNA) derived from its parents. So gametes are haploid. Union of two gametes and fusion of their nuclei result in the doubling of the DNA content in the zygole, which is hence diploid. All cells derived from the zygote are diploid. Thus, each offspring is not a mere duplicate of a single parent but is the product of the interaction of various genes (DNA) contributed by both mother and father. This results in genetic variation which is important from the point of view of evolution and adaptation. Thus, though an individual dies, it perpetuates itself by the process Of reproduction, and the race continues.
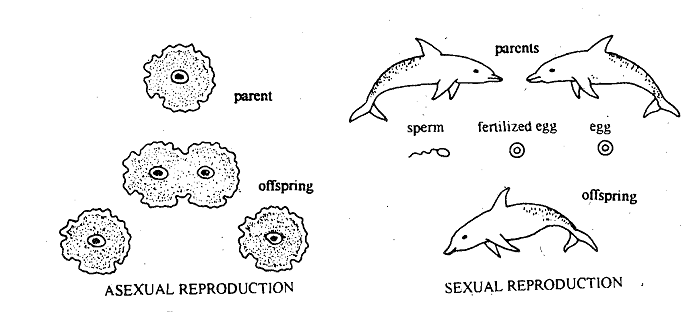
Figure: Approaches to reproduction - (a) in asexual reproduction, one individual gives rise to offsprings which are identical to the parent. (b) In sexual reproduction, each parent contributes a sex cell; these join to give rise to the offspring which thus has the genes and traits of both parents.