Under this section we will be looking at the previous case for the constant coefficient and linear and homogeneous second order differential equations. In this case we need solutions to,
ay′′ + by′ + cy = 0
Here a solution to the characteristic equation is as:
ar2 + br +c = 0
Such are double roots r1 = r2 = r.
This leads to a problem though. Recall which the solutions are as
y1(t) = er1t = ert, and y2(t) = er2t = ert
These are similar solution and will NOT be "nice enough" to create a general solution. I promise that I'll describe "nice enough"! Consequently, we can utilize the first solution, although we're going to require a second solution.
Before determining this second solution let's take some side trip. The motive for the side trip will be clear finally. By the quadratic formula we identify that the roots to the characteristic equation as,
r1,2 = (- b + √(b2 - 4ac))/2a
In this case, as we have double roots we should have,
b2 - 4ac = 0
It is the only method which we can get double roots and under this case the roots will be,
r1,2 = (- b)/2a
Thus, the one solution that we've found is,
y1(t) = e-(bt/2a)
To determine a second solution we will use the fact as constant times a solution to a linear homogeneous differential equation is also a solution. If it is true so maybe we'll get lucky and the subsequent will also be a solution,
y2(t) = n(t) y1(t) = n (t) e-(bt/2a)
Along with a proper option of v(t). To find out if this in fact can be done, let's plug this back in the differential equation and notice what we find. We'll first require a couple of derivatives.
y2'(t) = n' e-(bt/2a) - (b/2a) n e-(bt/2a)
y2''(t) = n'' e-(bt/2a) - (b/2a) n'e-(bt/2a) - (b/2a) n'e-(bt/2a) +(b/4a2) ne-(bt/2a)
= n'' e-(bt/2a) - (b/a) n'e-(bt/2a) +(b/4a2) ne-(bt/2a)
We dropped the (t) part upon the v to simplify things some for the writing out of the derivatives. Here, plug these in the differential equation.
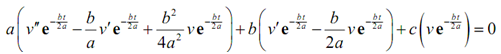
Let's do factor an exponential out of all the terms so we get. We'll also get all the coefficients of v and also its derivatives,
e-(bt/2a) ((an'' + (- b + b) n') + ((b/4a2) - (b/2a) + c )) = 0
e-(bt/2a) ((an'' +(-(b/4a2) + c) n ) = 0
e-(bt/2a) ((an'' - (1/4a) (b2 - 4ac) n ) = 0
Now, since we are working along with a double root we identify that that the second term will be zero. Also exponentials are never zero. Thus, (1) will be a solution to the differential equation given v(t) is a function that satisfies the subsequent differential equation.
av′′ = 0 OR v′′ = 0
We can drop the a since we identify that this can't be zero. If this were we wouldn't have a second order differential equation! Thus, we can now agree on the most general possible form which is allowable for v(t).
v′ = ∫ v′′ dt = c, v (t )= ∫ v′ dt = ct + k
This is in fact more complicated than we require and actually we can drop both of the constants from that. To notice why this is let's go ahead and utilize this to find the second solution. The two solutions are so,
y1(t) = e-(bt/2a), and y2(t) = (ct + k) e-(bt/2a)
Finally you will be capable to show that these two solutions are "nice enough" to create a general solution. The general solution would after that be as
y(t) = c1e-(bt/2a)+ c2(ct+ k) e-(bt/2a),
= c1e-(bt/2a)+ (c2ct+ c2k) e-(bt/2a),
= (c1+ c2k) e-(bt/2a) + c2ct e-(bt/2a),
See here that we rearranged things a little. Here, c, k, c1, and c2 are all unknown constants thus any combination of them will also be unknown constants. In exacting, c1+c2 k and c2 c are unknown constants consequently we'll just rewrite them as given below,
y1(t) = c1e-(bt/2a)+ c1te-(bt/2a)
Therefore, if we go back to the most general form for v(t) we can let c=1 and k=0 and we will arrive at similar general solution.
Let's recap. If the roots of the characteristic equation are as r1 = r2 = r, so the general solution is here
y (t ) = c1ert+ c2tert
Here, let's work a couple of illustrations.
Example 1: Solve the subsequent IVP.
y′′ - 4 y′ + 4 y = 0
y (0) = 12
y′ (0) = -3
Solution
The characteristic equation and its roots are.
r2 - 4r + 4 = ( r - 2)2 = 0
r1,2 = 2
The general solution and its derivative are as
y (t ) = c1 e2t + c2te2t
y′ (t) = 2c1e2t + c2e2t + 2c2te2t
Keep in mind that to product rule the second term! Plugging in the initial conditions provides the as given system.
12 = y (0) = c1
-3 = y′ (0) = 2c1 + c2
This system is simply solve to find c1 = 12 and c2 = -27. The actual solution to the Initial Value Problem is then.
y (t ) = 12e2t - 27te2t