RELATIONSHIP WITH 8 VARIANTS OF NATIONAL PRODUCT AGGREGATES
We have shown the distinction between national product at market prices and national product at factor cost, based on whether or not net indirect taxes have been included. And there is also a distinction between gross or net national product according to whether investment is inclusive of capital consumption or not. Further, a distinction has been drawn between domestic and national product, according to whether we are measuring net factor income from abroad (i.e. the net return on factors owned by nationals of the country concerned) or whether we are measuring what is produced within the domestic economy. This implies that there are eight possible combinations of national product aggregates, as shown below.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) at market prices (MP)
at factor cost (FC)
Gross National Product (GNP) at market prices (MP)
at factor cost (FC)
Net Domestic Product (NDP) at market prices (MP)
at factor cost (FC)
Net National Product (NNP) at market prices (MP)
at factor cost (FC)
The way that these national product aggregates are related to each other can be understood from the figure 3.2.
Figure 3.2
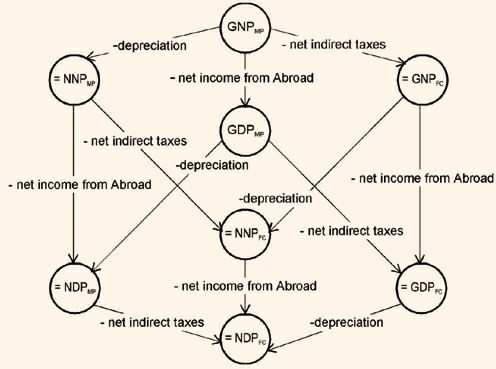
We can sum up the differences between gross and net, market prices and factor cost and national and domestic concepts in the following way:
Gross=Net + Depreciation
Market Prices=Factor Cost + [Indirect Taxes - Subsidies]
National=Domestic + Net Factor Income from Abroad
There are some national product aggregates that are more frequently met with and we have several ways of ordering them. One of these is as follows:
i. Gross domestic product at market price + net factor income from abroad equals
ii. Gross national product at market prices - net indirect taxes (indirect taxes - subsidies) equals
iii. Gross national product at factor cost - capital consumption (depreciation) equalsiv. Net national product at factor cost, which is popularly known as national income.