REASONS FOR FLUCTUATIONS IN AGRICULTURAL PRICES
Production depends on factors beyond the control of the producers e.g. weather, disease and pests. Actual and planned output is often not the same and the price charged is usually different from the expected price.
i) The production of these products depends on factors beyond the control of the producers e.g weather, diseases and pests, consequently, actual output is often not the same as planned output and hence the actual price is usually different from the expected price. At any one time the supply of the commodity will be perfectly inelastic.
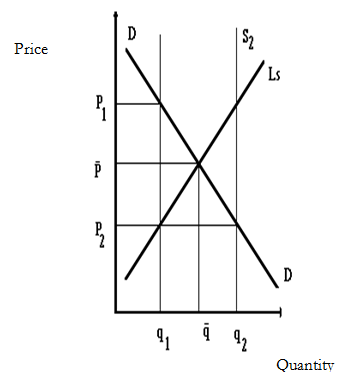
DD is the demand curve and Ls the long run supply curve indicating what producers will be willing to produce and sell at different prices if production was entirely under their control. Thus, P is the expected equilibrium prices and q the planned equilibrium quantity. Depending on the external factors mentioned above, actual output may be than planned output e.g. at q2 making the price p2 or less than planned output e.g. at q1 making the price P1.
The situation is made worse by the fact that these commodities are not easily stored, so that if the actual output falls short of planned output it cannot be supplemented from the stocks and if the actual output is greater than planned output it cannot be reduced which would prevent prices from being too low.
Besides the short run elasticity of supply is low, since once a given amount of the crop has been planted it is comparatively difficult to increase or decrease the resulting output. Hence high (or low) prices are likely to persist in the short term before additional supply can be made available
Furthermore the demand for these products is also price inelastic, for they are either foods or raw materials, and in the latter case they usually form a small proportion of the total inputs. Thus, if actual output is in excess of planned output, it is difficult to sell off the excess without depressing prices excessively.
Equilibrium prices may also be difficult to attain because of lagged responses by producers to respond to price changes. In this case it is assumed that though producers are continually disappointed they never become wiser as a result and thus precipitate the price movement and that stocks of the commodity are not stored by producers or middle men in periods of low prices to be resold in periods of, otherwise high prices thus ironing out the unevenness of supply and price. This leads to the cobweb theorem (A dynamic model of supply and demand in which adaptive (or non-rational) expectations lead to perpetual oscillations in prices)