Rails:
Rails are the part of the Permanent Way on which the wheels of the train travel. The rails also maintain the gauge separation.
Rails have to possess the following desirable properties:
(a) High strength
(b) Good flexural stiffness
(c) Good durability and less wear and tear
(d) Sufficient contact area with the wheel flange
(e) Sufficient contact area with the sleeper
(f) Rounded fillets
Flat-footed rails are now commonly used in India (Figure).
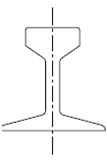
Figure: Flat Footed Rail
The standard rail section used for BG high speed lines and heavy traffic is 60 Kg/m while for BG medium speed and low traffic, a rail 52 Kg/m is adequate.
Standard rails come in a length of 13 m. Thus, it is necessary to join the two rails by a fish plate (Figure).
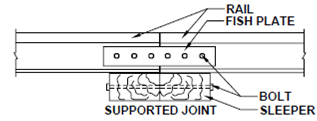
Figure : Fish Plate at Rail Joint
Since rail joints result in wear and tear of rails and create discomfort (sound and jerks) to passengers, the modern practice is to avoid joints by welding. An expansion gap is provided at the ends.