Quality Improvement methodology
For Quality Improvement, the Plan-Do-Check-Act cycle approach is generally used. The PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle also called the Deming cycle is as shown in the figure below:
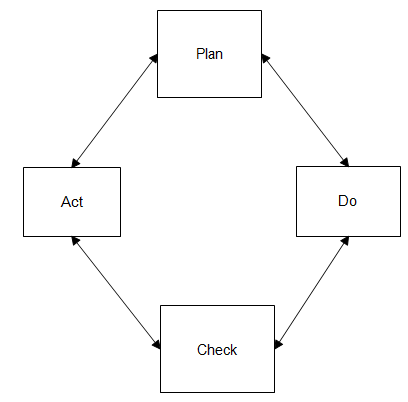
Figure : Plan-Do-Check-Act cycle
The Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle is as follows:
- Plan: This is the beginning point where the process will have to be selected. This process if executed correctly indicates the greatest opportunity for success, at first; it may be useful to select the process which indicates the biggest potential for the successful improvement and also maybe the "easiest" one. The team may face less difficulty while working through the model the first time, and both the team and the management will be encouraged by the success. After selecting the right process, the change should be analysed and planned.
- Do: This is the "action-oriented" step. The results can be critical for further quality improvement.
- Check: This step observes the effect of the change. It is usually the careful and a comprehensive study of the results. The project team should fully understand the effects of the change and also understand its occurrence, and also how it may affect some other processes in the system.
- Act: This is to check if the results are as expected and if they show the required beneficial effect, and also implement the change system-wide. The test case will show that the change might probably work as planned, so there will be little risk of knee-jerking the work force. This is a cycle which supports the continual improvement which signifies when to start the cycle again.
The quality life cycle consists of the customer, requirement, specification, quality assurance activity, quality assurance plan, quality control and PDCA and is as shown in the Figure 9.2.
1. Customer - Customers are the base of the quality cycle and can be classified as internal, external and hidden.
2. Requirement - Customers are the sources of requirements. The requirements have to be full-filled for the project's success.
3. Specification - Specifications have to be given by the customer in the contract or will be given informally by other customers.
4. Quality assurance activity - Quality assurance is the application of planned and systematic quality activities to make sure that all the processes required for the project are employed to meet the requirements.
5. Quality assurance plan - Quality assurance plan documents all the activities and allows for the effective management.
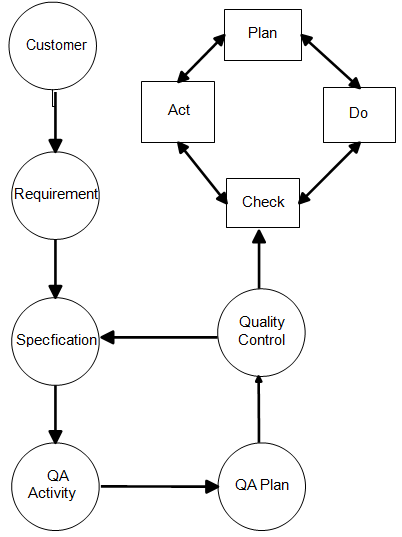
Figure : Quality Cycle
6. Quality control - Quality control is used to check the quality of the deliverables with the application of complex tools.
7. PDCA - Plan DO Check Act (PDCA) cycle is used to check the quality improvement.