Purchasing power parity:
When PPP holds, the domestic currency has the same purchasing power at home and in any other country. PPP also implies that a foreign currency will depreciate if the country's price level rises relative to the foreign price level and appreciate if the foreign price level rises relative to the country's own price level. The question is, does the PPP hold in reality. The empirical evidence seems to suggest that it does not always hold particularly in the short run. The reason is that there are substantial transaction costs. Moreover, goods are really not identical across markets and countries. There are also substantial amount of non-traded goods. But the PPP does a good job of explaining the direction of change in the exchange rate. Now let us try to look at the determinants of exchange rates in the short run. In the short run, there is tremendous volatility and fluctuations in exchange rates. The determinants of exchange rates in the long run do not explain the fluctuations in exchange rates in the short run. Since in modern times foreign exchange markets are linked with computers, banks and other dealers can very quickly convert domestic currency into foreign currency, they can very quickly buy at a lower price in one market and try to sell in the same or other market very soon. Thus in the short run, exchange rates are largely determined by expectations of future exchange rates.
Banks and other traders of currency are continually seeking out profit opportunities. To them foreign bank deposits are close substitutes for deposits in foreign currency because these can be easily converted from one currency to another via the foreign
exchange market. So these dealers are constantly monitoring movements of interest rates and exchange rates to determine the most profitable kind of deposits to hold.
If Eet+1 denotes the trader's expectations of the future exchange rate, and et the current exchange rate, then the expected rate of return of holding foreign deposits is:
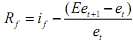
If id is domestic interest rates, traders are continually comparing id with Rf . if the latter is greater, then the traders will like to hold deposits abroad. They switch continually across countries to maximise their expected returns, and this goes on until in equilibrium
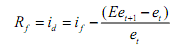
This relation is called interest rate parity, because it depicts the equality of interest rate on domestic deposits and expected return on foreign deposits. When interest rate parity holds, traders cannot profit by switching currency holdings, and this effectively determines the short run current exchange rate et.
The interest rate parity relation shows that Rf depends not only on et and If but also on traders' expectations about future exchange rates Eet+1 . traders are continually updating this expectation based on all the relevant current information. Hence, short run exchange rates are hard to predict and arise mainly due to traders' minute-to- minute changes in expectations that take place as new information becomes available.