Properties of Some Fibres
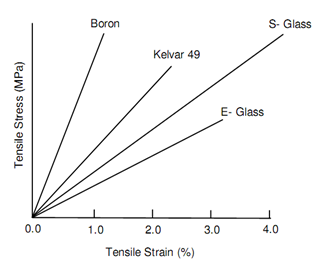
Figure: Properties of Some Fibres
Matrix of varied nature materials can be employed with various fibres. Kevlar, C and glass fibres are in common employing. Carbon fibres can be utilized in C, metals, plastics, glass and ceramics. C and Glass are brittle and metals are heavy and they do not wet carbon fibre well also. Ceramics have extremely dissimilar type coefficient of thermal expansion and their greatest quality of high temperature resistance cannot be utilized in relation of carbon fibres. Plastics, thus, are the suitable matrix material for carbon fibres.
The plastics utilized as matrix materials comprise polyesters, polymides, thermoplastics, epoxies and phenolics. Such materials still have great restriction in respect of temperatures. Thermoplastics and Polyesters can be utilized only upto 100oC. Epoxies can be employed upto 150oC. Phenolics can be employed upto 250oC. Though, Phenolics, have poor mechanical properties. Polymides are superior at temperature higher than 200oC but certainly not usable near to 400oC. Table no.3 compares two commonly utilized matrix materials along with glass, kevlar and carbon fibres. Epoxies mostly suit carbon fibres more than any other matrix material due to very good adhesion.
Table no.3: Properties of Unfilled Cast Epoxy and Polyester
|
Sl. No.
|
Property
|
Epoxy
|
Polyester
|
|
1
|
Tensile Strength (MPa)
|
55-130
|
40-90
|
|
2
|
Modulus of Elasticity (Tension) GPa
|
2.8-4.2
|
2.0-4.4
|
|
3
|
Impact Strength (J/m)
|
5.3-53
|
10-21
|
|
4
|
Density (kg/m3)
|
1100-1460
|
1200-1300
|
|
5
|
Maximum Use Temperature
(oC)
|
150oC
|
100oC
|
Epoxy resins have superior strength, higher cost and employed as matrix for aramid fibres and carbon fibres. As composites their usual applications are in marine, automotive and aerospace engineering, and for their high strength/weight ratio, in these regions carbon fibre reinforced composites are replacing metallic materials. Along the length of fibres such composite can improve a tensile strength of about 1800 MPa along with modulus of elasticity of 145 GPa. Conversely, their percent elongation is limited to just 1.2 percent. Unidirectional composites have extremely low transverse strength and modulus of elasticity. Overall enhancement in properties is realized by combining unidirectional laminates at different angles as represented in following figure.