Program Insertion of a node into any Circular Linked List
Figure depicts a Circular linked list from which an element was deleted.
ALGORITHM (Deletion of an element from a Circular Linked List)
Step 1 Begin
Step 2 if the list is empty, element cannot be eliminated.
Step 3 else, if element desire to be deleted at first node, then make the start (head) to point to the second element.
Step 4 else, Removeelement from the list by calling find function & returning the found address of the element.
Step 5 End.
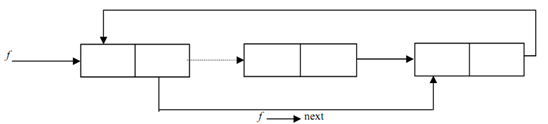
Figure: A Circular Linked List through which an element was deleted
(Dotted line indicates the linked that existed prior to deletion)
Program demonstrated the code for the deletion of an element from the Circular linked list.
#include
#include
#define NULL 0
structlinked_list
{
int data;
structlinked_list *next;
};
typedefstructlinked_listclist;
clist *head, *s;
/* prototype of find and delete_function*/
clist * delete_clist(clist *);
clist * find(clist *, int);
/*description of delete_clist */
clist *delete_clist(clist *start)
{
int key; clist * f, * temp;
printf("\n enter the element to be deleted \n");
scanf("%d", &key);
if(start->data == key)
{
temp=start->next; free(start);
start=temp;
}
else
{
f = find(start,key);
if(f==NULL)
printf("\n key not fund");
else
{
}
}
temp = f->next->next;
free(f->next);
f->next=temp;
return(start);
}
/*description of find function */
clist * find(clist *start, int key)
{
if(start->next->data == key)
return(start);
if(start->next->next == NULL)
return(NULL);
else
find(start->next, key);
}
void main()
{
voidcreate_clist(clist *);
int count(clist *);
void traverse(clist *);
head=(clist *)malloc(sizeof(clist));
s=head;
create_clist(head);
printf(" \n traversing the created clist and the starting address is %u \n", head);
traverse(head);
printf("\n number of elements in the clist %d \n", count(head));
head=delete_clist(head);
printf(" \n traversing the clist after delete_clistand starting address is following %u \n",head);
traverse(head);
}
voidcreate_clist(clist *start)
{
printf("inputthe element -1111 for coming out of loop\n");
scanf("%d", &start->data);
if(start->data == -1111)
start->next=s;
else
{
start->next=(clist*)malloc(sizeof(clist));
create_clist(start->next);
}
}
void traverse(clist *start)
{
if(start->next!=s)
{
printf("data is %d \t next element address is %u\n", start->data, start- traverse(start->next);
}
}
if(start->next == s)
printf("data is %d \t next element address is %u\n",start->data, start->next);
int count(clist *start)
{
if(start->next == s)
return 0;
else
}
return(1+count(start->next));
Program: Deletion of an element from the circular linked list