Production of Rotating Fields from Single-Phase Windings
In this subsection we show that a single-phase winding carrying alternating current produces a stationary pulsating flux that can be represented by two counterrotating fluxes of constant and equal magnitude.
Let us consider a single-phase winding, as shown in Figure(a), carrying alternating current i = I cos ωt . This winding will produce a flux-density distribution whose axis is fixed along the axis of the winding and that pulsates sinusoidally in magnitude. The flux density along the coil axis is proportional to the current and is given by Bm cos ωt , where Bm is the peak flux density along the coil axis.
Let the winding be on the stator of a rotating machine with uniform air gap, and let the flux density be distributed sinusoidally around the air gap. Then the instantaneous flux density at any position θ from the coil axis can be expressed as
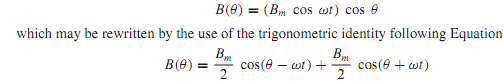
The sinusoidal flux-density distribution given by Equation can be represented by a vector Bm cos ωt of pulsating magnitude on the axis of the coil, as shown in Figure. Alternatively, as suggested by Equation, this stationary pulsating flux-density vector can be represented by two counterrotating vectors of constant magnitude Bm/2, as shown in Figure. While Equation represents a standing space wave varying sinusoidally with time, Equation represents the two rotating components of constant and equalmagnitude,
rotating in opposite directions at the same angular velocity given by dθ/dt = ω. The vertical components of the two rotating vectors in Figure always cancel, and the horizontal components always yield a sum equal to Bm cos ωt , the instantaneous value of the pulsating vector.