Q. Principal categories in classification?
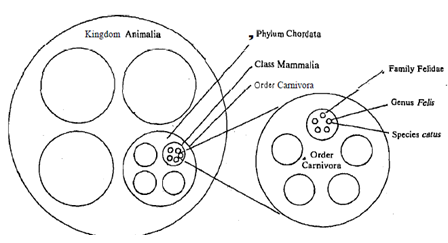
First of all there is a need to know what classification is? Let us define in simple term. Classification is placing of a plant (or groups of plants) Or animals (or groups of animals) in groups or categories according to a particular plan or sequence and in conformity with a nomenclatural system. Every species is classified as a member of a particular genus, the genus belongs to a family, family to an order, the order to a class and so on Fig.
In practical terms classification deals more with the placing of a plant group with a selected scheme than the placing of an individual plant in one of several minor categories. Thus a system of classification is necessary to allow us to identify plants and animals and to communicate scientifically with others. Indeed, classification is both an information storage and retrieval system without which scientific communication would be impossible. For instance a plant's name is the key that unlocks the door to its total biology. Ecologists, horticulturists, biochemists, agriculturists and others must have a reference system for the plants, they use in their research. However, the name of plant is not meant only for the scientist, it may be used by other people with varied interests and training, those who are interested in the natural history of plants. The scientific name of a plant communicates the species and genus, and from that the family may be easily determined.
From the time immemorial plants have been known by some name, they are common, vernacular or local names given by different persons. Thus a single plant . can bear several names, or several plants can be named by the same name at different places. For example, Verbuscum has 140 names Viola (pansy) has more than150 names, Plant ago (plantain) has about 50 names. Some common names such as 'celaf., Foxtail, flame of the forest are being used for variety of plants markedly different from each other. It is, therefore, apparent that in order to avoid confusion some general principles of universal acceptance had to be adopted. Thus professional botanists gradually suggested names to all the known plants and classified them scientific way. The scientific names and classification are published and remain unchanged - in different languages and are quoted as such universally in botanical ' 8 literature We will take an example and see how classification helps its user. For example, when a forester identifies a white oak (Quercus alba), it can reasonably be assumed that there are other individual white oaks in nature that have similar morphological features, structure and physiology. The knowledge that a plant is Quercus alba automatically predicts that much information will be applicable to that plant.