Prim's algorithm employs the concept of sets. Rather than processing the graph by sorted order of edges, this algorithm processes the edges within the graph randomly by building up disjoint sets.
It employs two disjoint sets A and A. Prim's algorithm works by iterating through the nodes and then determining the shortest edge from the set A to that of set A (that means outside A), followed by the adding up the node to the new graph. While all the nodes are processed, we have a minimum cost spanning tree.
Instead building a sub-graph by inserting one edge at a time, Prim's algorithm builds tree one vertex at a time.
The steps in Prim's algorithm are as:
Consider G be the graph having n vertices for which minimum cost spanning tree is to be made.
Consider T be the minimum spanning tree.
consider T be a single vertex x.
while (T has fewer than n vertices)
{
find the smallest edge connecting T through G-T
add it to T
}
Let the graph of Figure. And another Figure shows the various steps involved in the construction of Minimum Cost Spanning Tree of graph of this Figure
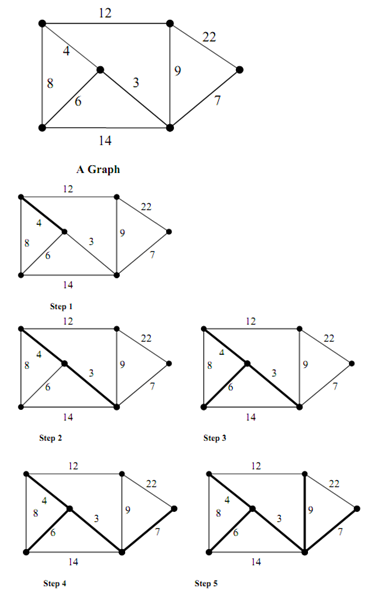
Figure: Construction of Minimum Cost Spanning Tree for the Graph of Figure by application of Prim's algorithm
The following are several steps in the construction of MST for the graph of Figure via Prim's algorithm.
Step 1: We start along a single vertex (node). Now the set A has this single node and set A has rest of the nodes. Add the edge along the lowest cost from A to A. The edge along cost 4 is added.
Step 2: Lowest cost path through shaded portion of the graph to the rest of the graph (edge along cost 3) is chosen and added to MST.
Step 3: Lowest cost path through shaded portion of the graph to the rest of the graph (edge with cost 6) is chosen and inserted to MST.
Step 4: Lowest cost path from shaded portion of graph to the rest of the graph (edge along cost 73) is chosen and added to MST.
Step 5: The next lowest cost edge to the set not in MST is 8 but makes a cycle. So, it is discarded. The next lowest cost edge 9 is inserted. Now the MST has all the vertices of the graph. This results in the MST of the original graph.
Comparison of Kruskal's algorithm & Prim's algorithm
|
|
Kruskal's algorithm
|
Prim's algorithm
|
|
Principle
|
Based on generic minimum cost
spanning tree algorithms
|
A special case of generic minimum
cost spanning tree algorithm. Operates like Dijkstra's algorithm for finding shortest path in a graph.
|
|
Operation
|
Operates on a single set of
edges in the graph
|
Operates on two disjoint sets of
edges in the graph
|
|
Running time
|
O(E log E) where E is the
number of edges in the graph
|
O(E log V), which is
asymptotically same as Kruskal's algorithm
|
From the above comparison, it might be observed that for dense graphs with more number of edges for a given number of vertices, Prim's algorithm is more efficient.