Potential of Parallelism
Problems in the actual world differ in respect of the degree of natural parallelism inherent in the personal problem domain. Some problems may be simply parallelized. On the other hand, there are some natural sequential difficulty (for ex: - computation of Fibonacci sequence) whose parallelization is almost impossible. The extent of parallelism may be enhanced by appropriate design of an algorithm to explain the problem consideration. If processes don't split address space and we could remove data dependency among instructions, we can attain higher level of parallelism. The idea of speed up is used as a calculate of the speed up that point out up to what degree to which a sequential program can be parallelised. Speed up may be occupied as a sort of point of inherent parallelism in a program. In this admiration, Amdahl has specified a law, known as Amdahl's Law, which declare that potential program speedup is distinct by the fraction of code (P) that preserve be parallelised:
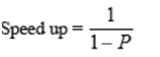
If no element of the code can be parallelized, P = 0 and the speedup = 1 i.e. it is an essentially sequential program. If every code is parallelized, P = 1, the speedup is infinite. But basically, the code in no program can made 100% parallel. Hence speed up can never be immeasurable.
If 50% of the code is parallelized, maximum speedup = 2, meaning the code will scamper twice as fast. If we establish the amount of processors performing the parallel fraction of work, the link can be modelled by:
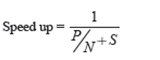
Where P = parallel fraction, S = serial fraction and N = number of processors. The Table 1 shows the value of speed up for different values P and N.
Table 1
Speedup
--------------------------------
N P = .50 P = .90 P = .99
----- ------- ------- -------
10 1.82 5.26 9.17
100 1.98 9.17 50.25
1000 1.99 9.91 90.99
10000 1.99 9.91 99.02
The Table 1 suggest that speed up increase as P increases. However, after a definite Limits N does not have a lot impact on the value of pace up. The reason being that, for N processors to remain dynamic, the code must be, in some way or other, being divisible in, independent part, roughly N parts each part taking almost same total of time.