Q. Physical Properties of group16?
Similar to the groups discussed earlier. The metallic character in Group 16, increases with increasing atomic number. Oxygen and sulphur are entirely non-metallic in their chemical behaviour. Selenium and tellurium, though essentially non-metallic, assume increasing metallic character and are termed as metalloids. Polonium is most metallic in the group.
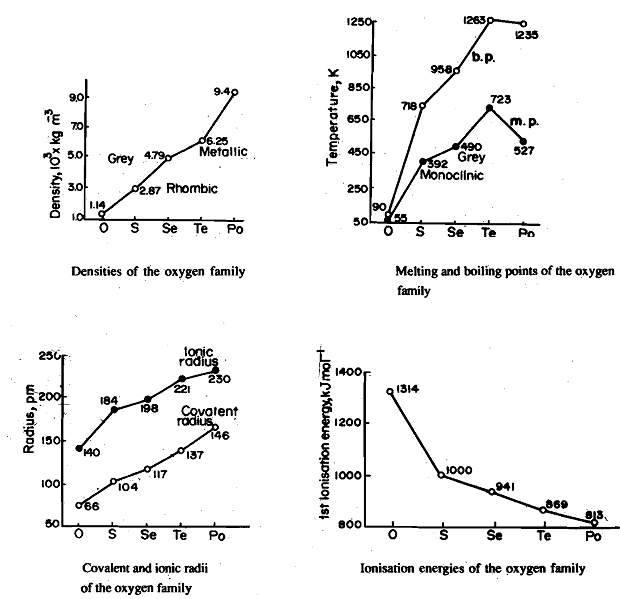
Density, Fig. 1, melting and boiling points. Fig. 2, covalent and ionic radii, Fig 3 shows a regular increase from oxygen to polonium. The large difference in melti, /g and boiling points between oxygen and sulphur can be explained on the basis of their structure. Oxygen exists mostly as a diatomic molecule held together by weak van der Waals forces while others exist as polyatomic molecules, e.g., S8 , Se8, etc.. Where the ate-ms are bonded by c6valent bonds associated with high dissociation energy. Their existence as diatomic and polyatomic molecules can be explained as follows. The bond energy of the oxygen-oxygen double bond, 0=0, is 498 kJ mol-1. This makes the 0=0 bond more than three times as strong as the SO bond (bond energy for 0-0 is 142 kJ mol-1). By comparison the S=S bond is less than twice as strong as the S-S single bond (bond energy for S=S, 43tkJ mol-1; S-S, 264 kJ mol-1). This results in catenated -0--0-0- chains being unstable relative to 0=0; but catenated -S-S-S- chains being stable relative to the molecule S=S.
The elements of Group 16 are characterised by high ionisation energies, Fig. 9.7, decreasing gradually from oxygen to polonium. The high values indicate reluctance of these elements to form cations. Their electro negativities decrease with increasing atomic number. Thus, in view of the fall in electronegativity, metallic character' within the group increases with increasing atom size.
Oxygen, the second most electronegative element, fluorine being the first has a strong tendency to accept two electrons and give 02- ion. Thus; almost all metal oxides am ionic and contain 02- ions. Usually oxygen exhibits an oxidation state -2 in its other compounds also. It exhibits positive oxidation states only in a few compounds formed with fluorine, i.e., OF, and O,F,. The tendency for the formation of divalent anions deceases from sulphur downwards because of the increasing size and decreasing electronegativity of the el-i' Sulphur, selenium and tellurium show a' tendency for covalency with formal oxidation states +2,+4 and +6 in compounds in which they are combined wit), more electronegative elements such as oxygen and halogens. You may note that in the higher oxidation state of +4 and +6 of these elements electrons are unpaired and promoted to vacant d orbitals.
Oxygen, and to a greater extent, 'sulphur differ from the other members of the group in their ability to catenae and form peroxides, H-0-0-H and polysulphides, H2 Sn, n=1-8, respectively. The strong tendency of catenation in sulphur is evident from the fairly high bond dissociation energy of S-S single bond (264 kJ m0l-I). As discussed earlier it is also reflected in the high melting and boiling points of sulphur.