Physical arrangement of resistors:
Before we look at some problems it is necessary to warn you that physical appearances can be deceptive. When components are mounted they are usually done so in a manner as to reduce the space they occupy to a minimum. Care must be taken to decide whether they are mounted in series or parallel or in a combination of both.
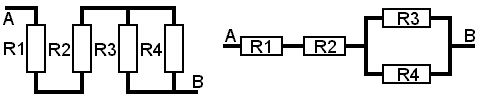
Thus on the Tag Board above, the resistors may appear to be in parallel, however, only R3 and R4 are in parallel.
SOLUTION OF RESISTOR NETWORKS USING OHM'S LAW
Many problems may be solved by combining series and parallel groups of resistors and applying Ohm's law. Remember that Ohm's law involves three quantities - I, V and R, thus to find any one quantity the other two must be known or be capable of determination. Where resistors appear in both series and parallel they may be reduced to a single effective resistance using a step-by-step sequence as follows.
• Combine any simple series groupings within branches ( R = R1 + R2 + --- ).
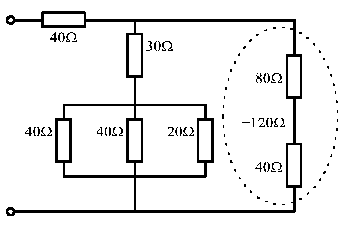
• Replace any simple parallel groups by single equivalent resistors 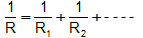
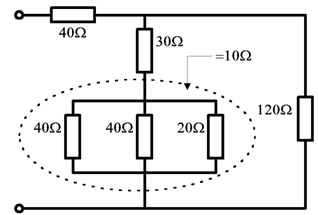
• Combine any simple series groupings ( R = R1 + R2 + --- ).
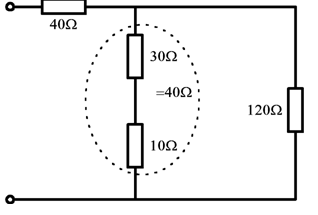
• Replace any simple parallel groups.
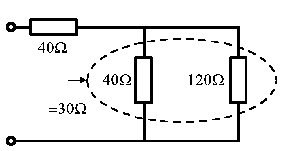
• Determine the single equivalent resistance.
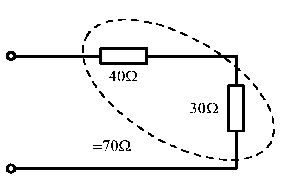
At this point the total circuit current (Is) may be found if Vs is given, or Vs found if Is is given. Having determined Vs or Is, as appropriate, the current in any branch and the voltage drop across any resistor can be found by working backwards through the sequence in the first paragraph of this section, applying Ohm's law at each stage.