The cell goes through many discrete phases before and after cell division. From this understanding, scientists then identified the four characteristic phases of the cell cycle:
G1 => S => G2 => M
1-G1(first growth or gap phase)
2-S (DNA synthesis phase)
3-G2 (second growth or gap phase)
4-M (mitotic phase)
G-1 Phase:
G 1 (Gap 1) is the period of extensive metabolic activity. Following events takes place during this phase:
- Cell normally grows in size.
- Specific enzymes are synthesized.
- DNA base units are accumulated for the DNA synthesis.
Go Phase:
Post-mitotic cell can exit the cell cycle during G 1 entering a phase called G o and remain for days, weeks. or in some cases (e.g. nerve cells and cells of the eye lens) even the life time of the organism without proliferating further.
S - Phase:
It is also called S-phase or synthesis phase, during which the DNA is synthesized and chromosomes number is doubled. Each chromosome now consist of two sister chromatids.
G 2 Phase:
It is also called pre-mitotic phase. During this phase cell is prepared for division. Following events takes place during this phase:
- Energy storage for chromosome movements.
- Mitosis specific proteins are produced.
- RNA and microtubule subunits for spindle fibers are synthesized.
Cell then proceed to next phase which is the period of division.
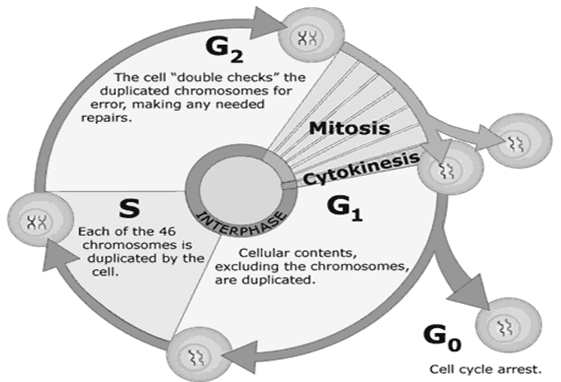
M Phase:
A nuclear division (mitosis) followed by a cell division (cytokinesis).
The period between mitotic divisions - that is, G1, S and G2 - is known as Interphase.