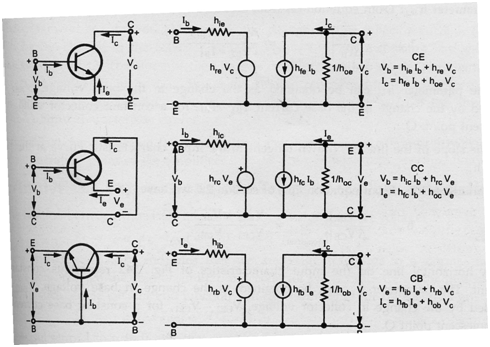
Partial derivatives - Transistor hybrid model:
The partial derivatives are taken by keeping the collector voltage or base current constant as pointed out by the subscript attached to the derivative.
ΔvB , ΔvC , Δ iC , Δ iB present the small signal(increment) base and collector voltages and currents, they are presented by symbols vb , vc , ib and ic correspondingly.
Eqs (3) and (4) may be written like as follow:
Vb = hie ib + hre Vc
ic = hfe ib + hoe Vc
in which hie =(∂f1/∂iB)Vc = (∂vB/∂iB)Vc = (ΔvB /ΔiB)Vc = (vb / ib)Vc
hre =(∂f1/∂vc)IB = (∂vB/∂vc) IB = (ΔvB /Δvc) IB = (vb /vc) IB
hfe =(∂f2/∂iB)Vc = (∂ic /∂iB)Vc = (Δ ic /ΔiB)Vc = (ic / ib)Vc
hoe= (∂f2/∂vc)IB = (∂ic /∂vc) IB = (Δ ic /Δvc) IB = (ic /vc) IB
The above equations described the h-parameters of the transistor in CE configuration. Similar theory can be extended to transistors in additional configurations.
Hybrid Model and Equations for the transistor in three dissimilar configurations are displayed below.