Operation of Algorithm
The following sequence of diagrams shows the operation of Dijkstra's Algorithm. The bold vertices show the vertex to which shortest path has been find out.
Step 1:
Initialize the graph, all of the vertices have infinite costs except the source vertex that has zero cost
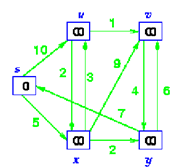
Step 2
From all the adjacent vertices, select the closest vertex to the source s.
As we initialized d[s] through 0, it's s. (illustrated in bold circle)
Add it to S
Relax all vertices adjacent to s, that means u & x
Update vertices u & x by 10 & 5 as the distance from s.
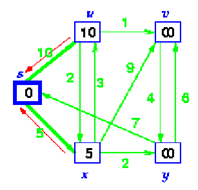
Step 3:
Select the nearest vertex, x. Relax all of vertices adjacent to x
Update predecessors for u, v & y. Predecessor of x = s
Predecessor of v = x ,s
Predecessor of y = x ,s
add x to S
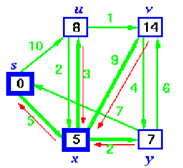
Step 4:
Now y is the closest vertex. Add it to S.
Relax v and adjust its predecessor.
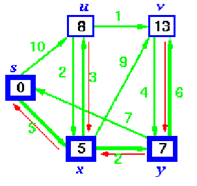
Step 5:
u is now closest, add it to S and adjust its adjacent vertex, v.
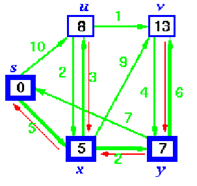
Step 6:
Finally, add v to S.
The predecessor list now defines the shortest path from each node to s.