Obtain the relevant authoritative literature on accounting for accounts receivable using the FASB's Codification Research System at the FASB website. What is the specific citation that describes disclosure of accounting policies for credit losses and doubtful accounts? List the disclosure requirements.
Accounting by FASB Codification
General
> Instruments
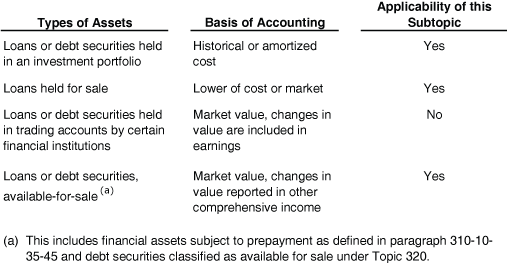
The following table outlines the applicability to various types of assets.
- Types of Assets Basis of Accounting Applicability of this Subtopic Loans or debt securities held in an investment portfolio Historical or amortized cost Yes Loans held for sale Lower of cost or market Yes Loans or debt securities held in trading accounts by certain financial institutions "Market value, changes in value are included in earnings" No "Loans or debt securities, available-for-sale (a)" "Market value, changes in value reported in other comprehensive income" Yes (a) This includes financial assets subject to prepayment as defined in paragraph 310-10-35-45 and debt securities classified as available for sale under Topic 320.
- a. Loans that are measured a fair valuer if all changes in fair value are included in earnings or, for an NFP, loans that are measured at fair value if all changes in fair value are included in the statement of activities and included in the performance indicator if a performance indicator is presented. Examples include those loans classified as trading securities.
- b. Mortgage loans classified as held for sale
- c. Leases. Only contracts that are classified by the purchaser as leases under that Topic meet this exclusion. The distinction between purchasing a lease and purchasing a stream of cash flows must be drawn to determine applicability of this Section.
- d. Loans acquired in a business combination accounted for at historical cost, including business combinations of two or more NFPs, the acquisition of a for-profit business entity by an NFP, and combinations of two or more mutual entities.
- e. Loans held by liquidating banks (financial reporting by liquidating banks
- f. Revolving credit agreements, such as credit cards and home equity loans, if at the acquisition date the borrower has revolving privileges.
- g. Loans that are a transferor's interests.
The substance rather than the form of the receivable shall govern. Receivables that may be involved in troubled debt restructurings commonly result from lending cash, or selling goods or services on credit. Examples are accounts receivable, notes, debentures and bonds (whether those receivables are secured or unsecured and whether they are convertible or nonconvertible), and related accrued interest, if any. Typically, each receivable is negotiated separately, but sometimes two or more receivables are negotiated together. For example, a debtor may negotiate with a group of creditors but sign separate debt instruments with each creditor.
Agriculture:
Patrons shall recognize patronage refunds on either of the following occasions:
- a. When the related patronage occurs if all of the following are probable:
- 1. A patronage refund applicable to the period will be declared.
- 2. One or more future events confirming the receipt of a patronage refund are expected to occur.
- 3. The amount of the refund can be reasonably estimated.
- 4. The accrual can be consistently made from year to year.
- b. On notification by the distributing cooperative.
The accrual shall be based on the latest available reliable information.
This Subtopic addresses financial-restructuring transactions by brokers and dealers in securities (broker-dealers).Specifically, a broker-dealer may make investments in the form of equity or provide financing to another entity in connection with financial-restructuring transactions. These investments may take many forms, including a direct investment or an investment in an entity (sometimes referred to as a bridge entity) that is established for the purpose of accumulating funds from several sources sufficient to make the investment.
55-1 Management may decide to dispose (by sale of swap) of loans prior to maturity for a number of reasons, including liquidity needs, tax considerations, portfolio diversification objectives, and management practices of generating loans specifically for disposition, in which case the loans shall be carried at the lower of cost (amortized historical cost less loan).
Statement of Assets and Liabilities or Statement of Net Assets
Receivables of Investment Companies
> Statement of Assets and Liabilities or Statement of Net Assets
>> Receivables
45-1 Receivables shall be listed separately at net realizable value for all of the following categories, among others:
- a. Dividends and interest
- b. Investment securities sold
- c. Capital stock sold
- d. Other accounts receivable, such as receivables from related parties including expense reimbursement receivables from affiliates, and variation margin on open futures contracts.
Land:
Disclosures by entities with retail land sales operations shall include all of the following:
- a. Maturities of accounts receivable for each of the five years following the date of the financial statements
- b. Delinquent accounts receivable and the method(s) for determining delinquency
- c. The weighted average and range of stated interest rates of receivables.
Credit Losses Citation and Disclosure Requirements:
45-1 This Subsection provides guidance on presentation matters for receivables, specifically:
- a. Loans or trade receivables
- b. Foreclosed and repossessed assets
- c. Allowances
- d. Bad-debt expense
- e. Discount and premium
- f. Unearned discounts
- g. Receivables classified as current assets
- h. Cash flows
- i. Receivables from officers, employees, or affiliates
- j. Note received as an equity contribution.