Application of the general suffix substitution closure theorem is slightly more complicated than application of the specific k-local versions. In the specific versions, all we had to do was to find two strings in which the same sequence of k - 1 adjacent symbols occurred which when cross-spliced witness the failure of suffix substitution closure. Here we have to be prepared for to show that for any k, such a pair of strings exist. Fortunately, we don't have to show that there is a single pair of strings that works for all k, only that for all k there is some pair. In other words, the pairs we use may depend on k. One useful way to organize this is known as an adversary argument. The theorem can be stated formally as:
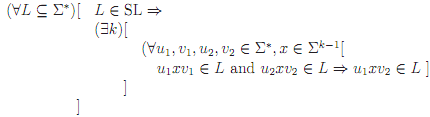
The idea is to interpret this as the rules of a game. You are attempting to show that the property does not hold; your adversary is attempting to show that it does. The universally bound variables (∀L) and (∀u , v , u , v , x) are your choices-your plays. The existentially bound variable (∃k) is your adversary's choice-their plays. The game proceeds from the outside of the formula in:
• You choose L the language you intend to prove is not SL.
• Your adversary, claiming that there is a k-local automaton that recognizes it, chooses k. Presumably, their choice of k will depend on your choice of L. Not even this adversary is going to claim that all languages are SL.
• You now choose two strings u1xv1 and u2xv2. Again, your choice should depend on the specific value of k your adversary chose (as well, of course, as the L you chose to start with).
• You win iff the two strings you chose witness that the language does not satisfy the theorem, i.e., iff
- u1xv1 and u2xv2 are both in L and
- u1xv2 is not in L.
Under this interpretation of the theorem, a proof that a given language is non SL consists of a strategy that always leads to a win whenever you start with L as your initial choice.