Suppose A = (Q,Σ, T, q0, F) is a DFA and that Q = {q0, q1, . . . , qn-1} includes n states. Thinking of the automaton in terms of its transition graph, a string x is recognized by the automaton iff there is a path through the graph from q0 to some qf ∈ F that is labeled x, i.e., if δ(q0, x) ∈ F. Suppose x ∈ L(A) and |x| = l. Then there is a path l edges long from q0 to qf . Since the path traverses l edges, it must visit l + 1 states.
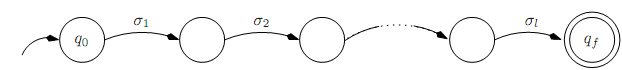
Suppose, now, that l ≥ n. Then the path must visit at least n+1 states. But there are only n states in Q; thus, the path must visit at least one state at least twice. (This is an application of the pigeon hole principle: If one places k objects into n bins, where k > n, then at least one bin must contain at least two objects.)
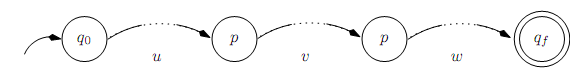
Thus, whenever |x| ≥ n the path labeled w will have a cycle. We can break the path into three segments: x = uvw, where
• there is a path (perhaps empty) from q0 to p labeled u (i.e., δ(q0, u) = p),
• there is a (non-empty) path from p to p (a cycle) labeled v (i.e., δ(p, v) = p),
• there is a path (again, possibly empty) from p to qf labeled w (i.e., δ(p,w) = qf ).
But if there is a path from q0 to p labeled u and one from p to qf labeled w then there is a path from q0 to qf labeled uw in which we do not take the loop labeled v, which is to say uw ∈ L(A). Formally
δ(q0, uvvw) = δ(δ(q0, u), w) = δ(p, w) = qf = F
Similarly, we can take the v loop more than once:
δ(q0, uvvw) = δ(δ(δ(δ(q0, u), v), v),w)
= δ(δ(δ(p, v), v),w)
= δ(δ(p, v),w)
= δ(p,w) = qf ∈ F.
In fact, we can take it as many times as we like. Thus, uvi
w ∈ L(A) for all i.
This implies, then, that if the language recognized by a DFA with n states includes a string of length at least n then it contains in?nitely many closely related strings as well. We can strengthen this by noting (as a consequence of the pigeon hole principle again) that the length of the path from q0 to the ?rst time a state repeats (i.e., the second occurrence of p) must be no greater than n. Thus |uv| ≤ n.