Nitrogen is very important constituents of all organisms life because it forms the structural parth of proteins, nucleic acids and chlorophyll molecules.
Earth 's atmosphere contains 79% of N2 but it can not be used by living organisms.it has to be combined with other elements (C,H Or O) to make it into usable form. Thus, nitrogen cycle is the biogeochemical cycle that describe the cycle flow of nitrogen and nitrogen containing compound in nature . it includes:
1.Fixation of Nitrogen in biosphere:
Three processes are invole for nitrogen fixation:
(i) Atmospheric fixation: combination of N2 and O2 into nitrogen oxide(NO,NO2, NO3) in presence of thunder lightening. These nitrogen oxide dissolve in rain forming nitrate.
(ii) Industrial fixation: combination of N2 and H2 in presence of cstalyst and high pressure and temperatures into NH3, which is used for making urea and ammonium nitrate (fertilizer.)
(iii) Biological fixation: involves conversion of N2 of air directly into organic nitrogen by symbiotic (present in leguminous plants) bacteria or some by free living bacteria.
Rhizobium bacteria
(a) N2 (air)  NO2 and NO3
NO2 and NO3
(Root modulus of peas/beans)
Azotobacters bacteria
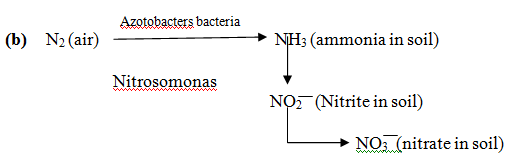
Plants utilize this NO3 ions for their growth and multiplication.
2. Nitrogen release into atmosphere:
Nitrogen cycle is completed by release of N2 back into atmosphere. Certain bacteria(pseudomonas and clostridium) in soil carry out denitrification process and convert nitrate back into nitrogen gas.
By anaerobic oxidation process, nitrate and ammonia are directly converted into gas.