Nitrogen Cycle:
Nitrogen is vital part of many essential organic compounds especially nucleic acids and proteins. It also forms a major part (79 per cent) of the atmosphere. In fact, the atmosphere is the chief reservoir of nitrogen, where it is present in the gaseous form,which unfortunately, cannot be directly used by plants and animals. Plants actually obtain their nitrogen from nitrates and ammonium salts in the soil to build up proteins, from which animals derive some of their proteins. The amount of nitrates and ammonium salts in the soil, is limited, at a given time, and their supply would quickly exhaust, if it were not for the renewal of supply of nitrogen which goes on continuously.
What are these processes which enable the cycling of nitrogen? Now, we shall discuss them briefly. You are advised to first look at the nine basic steps of nitrogen cycle as shown in Fig. When you see number 1 in the figure, for its explanation look up step 1 of the nitrogen cycle, described below.
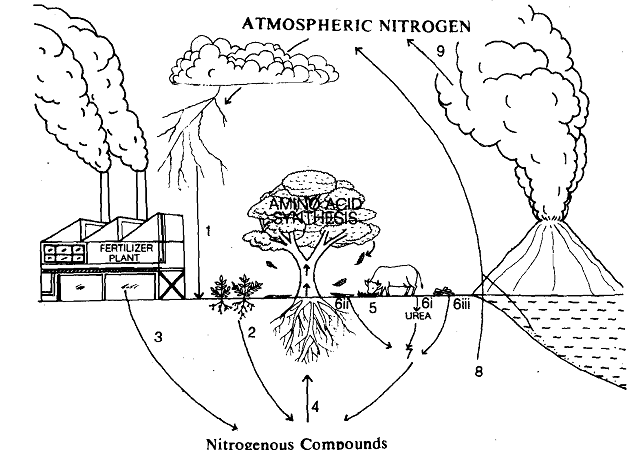
1) During thunderstorms, some of the oxygen and nitrogen in the air are converted into oxides of nitrogen by the high temperature of lightning. The oxides of nitrogen dissolve in rain water, reach the soil and get converted into nitrates. These nitrates are taken up by plants.
2) Certain bacteria can utilise atmospheric nitrogen and build up nitrates from it. They are called the nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Some of these bacteria live freely in soil, others live in small knots or nodules on the roots of certain plants. Surely, you must be familiar with plants such as beans, peas, peanuts, clover and alfa alfa etc., which have these bacteria canying nodules on their roots. Farmers make use of some of these plants, to make fodder, and then plough the rest of the plant into the soil, to increase the nitrates in the soil.
3) Nitrogen fixation by bacteria, i.e., the process of putting nitrogen in a form that plants can absorb, is rather slow, compared with the rate at which plants need nitrogen. In such a situation the demand for nitrogen is fulfilled by adding nitrogen containing fertilisers to the soil.
4) Nitrogen in the form of nitrates is taken up by plants, and is converted into amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins.
5) Nitrogen enters the food web through plants and passes on to animals which feed on them.
6) Nitrogen eventually returns to soil in the following ways: (i) During excretion, nitrogenous wastes in the form of various ammonium compounds are returned to the soil or water. (ii, iii) Nitrogen trapped in plants and animals returns to soil by death and subsequent decay of their bodies by the action of bacteria and fungi.
7) In soil, the nitrogen-containing matter are acted upon by bacteria and are converted to ammonium compounds, then eventually to nitrates.
8) Some soils, particularly the ones in bogs. estuaries, lakes and parts of the sea floor contain denitrifying bacteria which produce the opposite effect of nitrogen fixation.