Netfilter Firewall
Netfilter is the popular name for the packet filtering system installed by default in the Linux kernel. The filtering system can be used as a very effective stateful firewall. The iptables command is used to configure the filtering rules. The iptables commands are summarized in Table 5.1. The command allows for significantly more detailed rules, such as limiting the number of packets matching a rule per time period, even examining the data payload size. These details are outside the scope of this assignment. iptables rules are process in order, so the last rule should be to reject any other packets for outgoing traffic. A stateful firewall is one that examines sequences of packets. For example, in a typical TCP/IP session, several packets might be sent. Consider the following example where an external web browser accesses a web server (SYN, FIN, ACK are TCP flags, but the details are not important here):
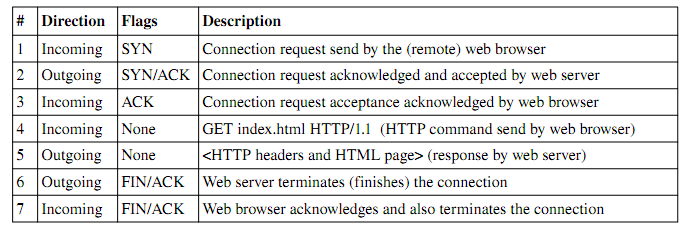
The first 3 messages constitute what is called the threeway handshake in TCP/IP. The two machines are negotiating terms of a temporary network connection. During this time, the state is considered NEW. After this process completes (successfully), the subsequent packets are considered ESTABLISHED. Sometimes, the web server will request that another connection is created (on another port, for example). The messages sent to this other connection are considered RELATED. RELATED and ESTABLISHED packets are generally considered valid. However, some (more detailed) firewalls will examine these packets for malicious data or suspicious activity. NEW packets are only accepted if they are sent to machines (i.e. destination IP addresses) which have a server open on that port (destination port number). Any NEW packets sent to other addresses/ports should be rejected.
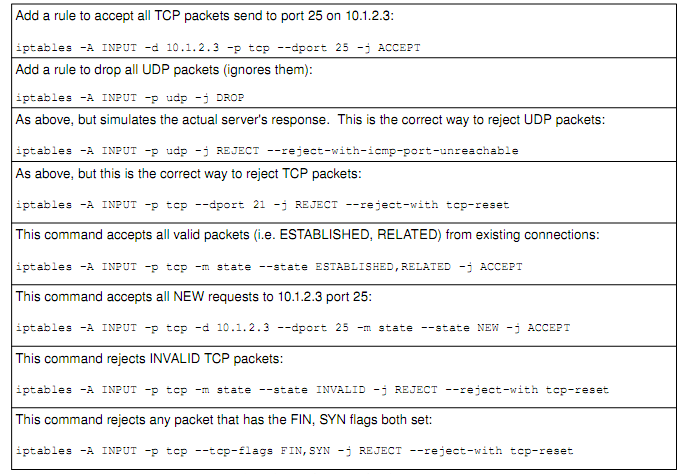
INVALID packets are packets that are trying to masquerade as valid packets (i.e. pretend they are part of another connection). These fool stateless firewalls, but since stateful firewalls keep track of valid connections, they can be easily discovered. INVALID traffic should never be accepted, since it is essentially always malicious in intent. Port scanning tools (such as nmap and amap) using various techniques to scan computers. Examples include connecting to each port (from 165535), trying to establish a TCP connection. This process puts entries into the log file, and tend to be red flagged by administrators. A more stealthy way to scan is to set certain weird combinations of flags in a TCP packet, and see how the server reacts. Many systems will respond if there is a server running on that port. This tells hackers a lot about the machine. For example, if there is a server on port 80, chance are it is a web server. The hacker can then try to find out more about the server on that port (by connecting with his/her browser, for example, and viewing the server HTTP header). Thus, such traffic should be dropped at the firewall, before it reaches the server.
Assignment Requirements
Note: It may be necessary to use man pages and other resources in order to complete this assignment.
- The firewall should have a dropbydefault policy
- Please use a POLICY (P) entry for this purpose, not a REJECT ALL rule
- Configure netfilter to restrict incoming traffic to only that which is required:
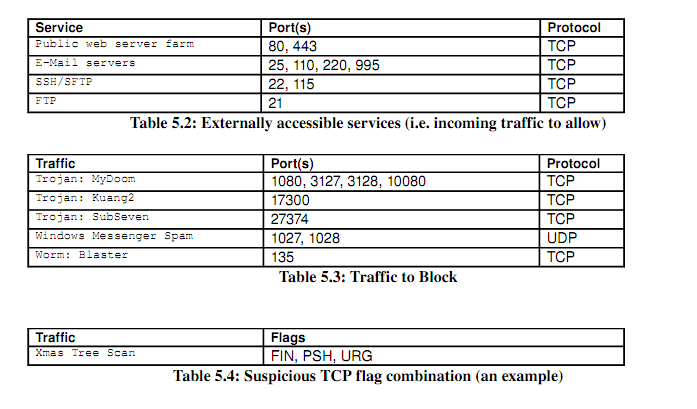
- These services are outlined in Table 5.2
- Configure netfilter to reject traffic to certain suspicious ports:
- These ports are outlined in Table 5.3
- Configure netfilter to block other scans and suspicious packets
- All traffic with suspicious TCP flag combinations, described in Table 5.4
- You only need to do one (the one shown), as a proof of concept
- Setup a script which contains these iptables commands
- Configure the boot scripts to execute this script on startup
- Verify that the firewall is in place by rebooting the VM and checking the iptables rules
- Perform a rulebyrule test of your firewall configuration using the nmap command
- Test each iptables rule individually with at least one nmap command
- The deliverables for this assignment include:
- A complete script of iptables commands (/etc/init.d/myfirewall)
- A directory listing wherever symbolic links to this script are placed
- A script of the nmap commands used to test the firewall.