Multiplexing and De multiplexing
Another critical set of services that are provided by the transport layer is that of application multiplexing and de multiplexing. This feature allows multiple applications to use the network simultaneously and ensure that the transport layer can differentiate the data it receives from the lower layer according to the application or process to which the data belong. To achieve this segment headers at the data segment headers at the transport layer have a set of fields to determine the process to which the segment data are to be delivered. At the receiver these fields are examined to determine the process to which the data segment belong and the segment it then directed to that process. This functions at the receiver transport layer that delivers the data it receivers to the correct application process is called de multiplexing. The process at the sender where information about the various active processes is collected and the corresponding information is incorporated in the segment headers to be given to the lower layers is called multiplexing
Transport layer multiplexing and de multiplexing that is extending the host to host delivery service provided by the network layer to a process to process delivery service for application running on the hosts. At the destination host layer has the responsibility of delivering the data in these segments to the appropriation process application process running in the host. As we have previously discussed that a process as part of a network application can have one or more sockets doors through which data passes from the network to the layer in the receiving host does not actually deliver data directly to a process but instead to an intermediary socket. Because at any given time there can be more than one socket in the receiving host each socket has a unique identifier. The format of the identifier depends on whether the socket in a UDP or in a TCP socket.
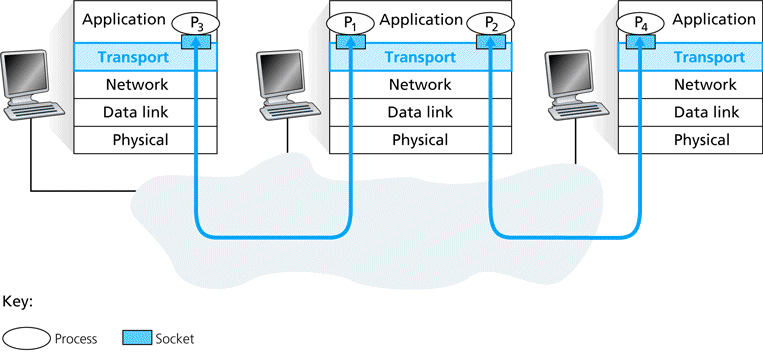
figure Multiplexing/ demultiplexing
Each transport layer segment receiving host has a set fields in the segment for directs an incoming transport layer segments to the appropriate socket. At the receiving end the transport layer examines these fields to identity the receiving socket and then directs the segment to that socket this job of delivering the data in a transport layer segment to the correct socket is called de multiplexing . the job of gathering data chunks at the source host form different and passing the segments to the network layer is called multiplexing. Note that the transport layer in the middle host in figure must de multiplex segments arriving.
From the network layer bellow to either process p or p above this is done by directing the arriving segments data the to the corresponding process socket. The transport layer in the middle host must also gather outgoing data from these sockets, form transport layer segments and pass there segments down to the network to the network layer.
Let us examine how transport layer multiplexing and de multiplexing is actually done in a host. We know that transport layer multiples in requires that sockets unique identifiers and that each segment have special fields that indicate the socket to which the segment is to be delivered. These special fields illustrated in figure are the source part number field and the destination port number filed. The port numbers ranging from 1 to 1023 are called well know port numbers and are restricted which means that they are reserved for use by well know application protocols such as HTTP which use post number 80 and FTP which use port number 21.
Service of transport layer de multiplexing each socket in the host can be assigned a port number and when a segment arrives to the host the transport layer examines the destination post number in the segment and directs the segments to the corresponding sockets. The segments data then passes through the sockets into the attached process.