Q. By giving an example show how multidimensional array can be represented in one the dimensional array.
Ans:
Multidimensional array: Multidimensional arrays can be defined as "arrays of arrays". For example, a bidimensional array may be imagined as a bidimensional table made of the elements, all of them of the same uniform data type.
int arr[3][5]; represents a bidimensional array of 3 per 5 elements of the type int. Similarly a three dimensional array such as
int arr[3][4][2]; represent an outer array of the three elements , each of which is a two dimensional array of the four rows, each of which is a one dimensional array of the five elements.
Multidimensional arrays are not restricted to the two or three indices (which means two dimensional or three dimensional). They may contain as many indices as required. Moreover the amount of memory needed for an array quickly increases with the each dimension.
For example: char arr [100][365][24][60][60];declaration would consume more than the 3 gigabytes of the memory.
The memory does not have rows and columns, so whether it is a one dimensional array or two dimensional arrays it does not matter, the array elements are stored linearly in the one continuous chain. For example, the multidimensional array
int arr[3][4][2]= {
{ {1,2},{3,4},{5,6},{7,8} },
{ {9,1},{1,2},{3,7},{4,7} },
{ {6,1},{18,19},{20,21},{22,23} },
}; is stored in memory just like the one-dimensional array as follows:
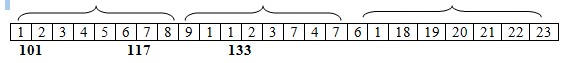
Multidimensional arrays are just an abstraction for the programmers, since we can obtain the same results with an easy array just by placing a factor between its indices.