Model Specification
We proceed with the model specification in the following steps.
1) The economy is composed of competitive firms (F in number) and identical workers (N in number). In each discrete time period a fraction 6 of the employed is laid off and joins the unemployment pool. The fraction 6 is called the 'rate of separation' in the literature. Firms hire workers from the pool, not directly from other firms.
2) The marginal cost of hiring for each firm is an increasing fimction of its level of hiring. This captures the idea that a high rate of hiring may force firms to increase their search intensity or, in a more general model with heterogeneous workers, to accept poor matches between workers and jobs. The marginal cost is also a decreasing function of aggregate unemployment - high aggregate unemployment makes it easier and cheaper for the firm to find willing and competent workers.
3) Since each firm chooses the rate of hiring by equating the marginal cost of hiring to the net marginal benefit of hiring, it is important to-determine, in the model, the marginal benefit of hiring to the firm. Assuming a firm to be risk neutral, the marginal value to the firm of a worker hired in this period is the expected present value of his marginal product so long as he works with the firm. The marginal value, denoted by q,, is therefore an infinite sum of discounted marginal productivities from the present period onwards to infinity. Two discounting factors are used on each term: one, as usual, to take account of time and the other to take account of the probability that a given worker will have left the job by time (t + i).
4) The net marginal benefit of hiring is equal to this marginal value minus the discounted present value of wages to be paid to the worker who is newly hired. It is in the spirit of search and matching models to assume that there is no labour market in which the wage is set -job matches require an explicit search process. The wage is set through bargaining so as to divide the surplus from the job between the worker and the firm. To simpli'fy matters, it is assumed in the present model that the worker experiences neither costs nor benefits from unemployment, so that the total surplus from the job is just the marginal value determined in paragraph 3 above. It is assumed that the worker obtains a share 5 of the surplus and the firm gets (1 - 6) with the size of 5 reflecting the bargaining power of the worker. Thus the marginal benefit of hiring to the firm is given as a fraction of the marginal value qt:
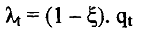
5) Each firm chooses the rate of hiring, h,, by equating the marginal benefit of hiring specified in paragraph 4 above with the marginal cost of hiring determined in paragraph 2 above