MODE OF HORMONE ACTION THROUGH EXTRACELLULAR RECEPTORS -
The molecules of amino acid derivatives, peptides or polypeptide (protein) hormones bind to specific receptor molecules located on the plasma membrane. The hormone-receptor complex causes the release of an enzyme adenylate cyclase from the receptor site.
This enzyme forms cyclic adenosine mono phosphate (cAMP) from ATP in the cell. The cAMP activates the existing enzyme system of the cell. This accelerates the biochemical reaction in the cell. The hormone is called the first messenger.
Earl W. Sutherland Jr (1915-1974) discovered cAMP in 1965. He got Nobel prize in physiology or medicine in 1971 for his discovery. "Role of cAMP in hormone action".
A detailed description of mode of hormone action through the extracellular receptors is given below :
The hormone insulin provides a good example to explain the mode of hormone action through the extracellular receptors. The membrane bound receptor of insulin is a protein consisting of four subunits : two a-subunits and two b-subunits. The two a-subunits protrude out from the plasma membrane (cell membrane) and bind insulin. The two b-subunits protrude into the cytoplasm of the cell. These receptors are usually less than 100 in most of our body cells but may be more than 1,00,000 as in some liver cells.
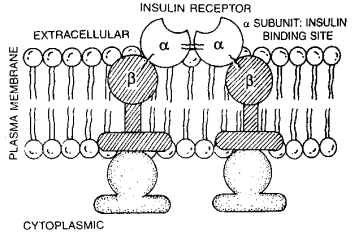
(i) Binding to the Receptor -
Insulin binds with the outer a-subunits of the receptor. This causes a structural change in the b-subunits, to become an activated kinase (tyrosine kinase). This kinase then promotes phosphorylation (addItion of phosphate groups) of many different substances inside the cell.
Most of the actions of insulin on the cell then result secondarily from these phosphorylation processes.
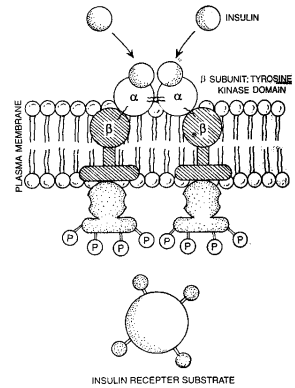
(ii) Second Messengers -
The mediator. A second example which is widely used in hormonal control of cell function is through adenylate cyclase. The hormone-receptor complex does not directly stimulates adenylate cyclase.
It is done through a transducer G protein. Alfred Gilmans has shown that the G protein is a peripheral membrane protein consisting of a, b and gsubunits. It interconverts between a GDP form and a GTP form.
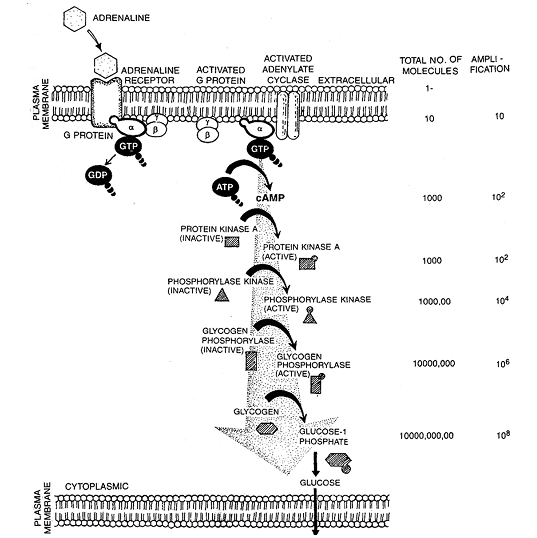
In muscle or liver cells, the hormones such as adrenaline bind receptor to form the hormone-receptor complex in the plasma membrane.
The hormone-receptor complex induces the release of GDP from the G protein. The a- subunit bearing GTP dissociates from bg subunit of G protein.
The activated bg - subunit of G protein activates adenylate cyclase. The activated adenylate cyclase catalyses the formation of cAMP from ATP.
G-protein activates an enzyme, phosphodiesterase. This enzyme makes phosphatidylinositol 4, 5-biphosphate (PIP 2) into a pair of mediators: inositol triphosphate (ITP or IP 3) and diacylglycerol (DAG or DG).
ITP and DAG are examples of second messengers. ITP is water soluble, therefore, diffuses into cytoplasm to release another messenger Ca2+ ions from intracellular endoplasmic reticulum activating many calcium-mediated processes. However, DAG remains in the plasma membrane where it activates an enzyme protein kinase C which activates many other enzymes like pyruvate dehydrogenase to bring about the physiological effects.
(iii) Amplification of Signal -
The increased level of cAMP activates the enzyme protein kinase A. Activated protein kinase A activates the enzyme, phosphorylase kinase.
Each molecule of protein kinase A activates about 100 molecules of enzyme phosphorylase kinase and so on. As a result a single molecule of adrenaline releases as many as 100 million molecules of glucose within only 1 or 2 minutes. However, a very small quantity of hormone is needed.
In a few instances, cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) which is only slightly different from cAMP acts in similar manner as a "second messenger".
(iv) Antagonistic Effect -
The effect of hormones which act against each other are called antagonistic effects.
Many body cells use more than one second messenger. In heart cells cAMP acts as a second messenger that increases muscle cell contraction in response to adrenaline, while cGMP acts as another second messenger which decreases muscle contraction in response to acetylcholinc.
Thus the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems achieve antagonise effect on heart beat. Another example of antagonistic effect is of insulin and glucagon. Insulin lowers blood sugar level and glucagon raises blood sugar level.
(v) Synergistic Effect -
When two or more hormones complement each other's actions and they are needed for full expression of the hormone effects are called synergistic effects.
For example, the production and ejection of milk by mammary glands require the sergistic effects of oestrogens, progesterone, prolactin and oxytocin hormones.
Thus it is evident from the above description that cAMP is not the only second messenger utilized by different hormones. Besides cAMP, certain other intracellular second messengers, as mentioned above, are cyclic gua- nosine monophosphate (cGMP), diacylglycerol (DAG), inositol triphosphate (ITP) and Ca2+.