Let's start things by searching for a mixing problem. Previously we saw these were back in the first order section. In those problems we had a tank of liquid with several kinds of contaminate dissolved in this. Liquid, possibly along with more contaminate dissolved in this, entered the tank and liquid left the tank. In this condition we need to extend things out to the following condition.
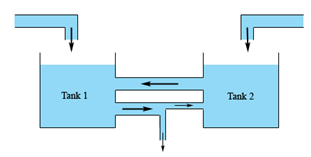
We'll here have two tanks which are interconnected along with liquid potentially entering both and along with an exit for some of the liquid if we require it (as exemplified by the lower connection). For this condition we're going to make the subsequent assumptions.
1. The outflow and inflow from each tank are equivalent, or conversely the volume in each tank is constant. While we worked with a particular tank we didn't need to worry regarding to this, but now if we don't well end up along with a system with nonconstant coefficients and those can be fairly difficult to solve.
2. The concentration of contaminate in all tanks are similar at each point in the tank. In actuality we know that it won't be true although without this assumption we'd require to deal with partial differential equations.
3. The concentration of contaminate in the outflow from tank 1 (the lower connection in the figure above) is similar as the concentration in tank 1. Similarly, the concentration of contaminate in the outflow from tank 2 that is the upper connection is similar as the concentration in tank 2.
4. The outflow from tank 1 is dividing and only some of the liquid exiting tank 1 in fact reaches tank 2. The remainder exits the system wholly. Remembered that if we don't need any liquid to wholly exit the system we can imagine of the exit as having a value which is turned off. Also note as we could just as easily do similar thing for the outflow from tank 2 if we'd needed to.