You might be aware of, and perhaps may have used, search engines such as Google to look for web pages on a topic of interest. The META Tag comes in useful if you want your web page to be easily locatable by search engines. When you enter a search string, the search engine shows web pages containing that string, provided the web page has used those in META tag appropriately. The search engine interacts with the META tag of the HTML page in order to find the required string. Information inside a Meta element should be such as to describe the document. Consider the following example (Figure 2.10).
<HTML>
<HEAD>
<TITLE>IGNOU</TITLE>
<META NAME="author" CONTENT="IGNOU">
<META NAME="description" CONTENT="This website shows you the different courses offered by
IGNOU">
<META NAME="keywords" CONTENT=" Website, different courses offered, IGNOU,mca,bca">
</HEAD>
<BODY>
<P>
The meta attributes of this document identify the author and courses offered.
</P>
</BODY>
</HTML>
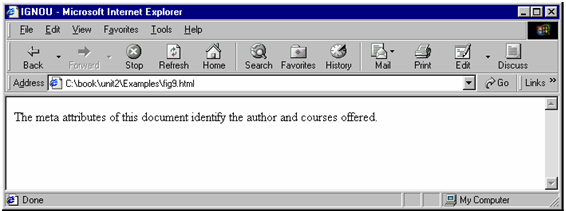
Figure: Using the META Tag
Meta tags contain two attributes:
a. NAME: This attribute is used for identifying the type of META tag you are including.
b. CONTENT: This attribute is used to specify the keywords that the search engine catalogs.
Consider the following code of the example illustrated in Figure
<META NAME= "description" CONTENT="This website shows you the different courses offered by IGNOU">
The CONTENT attribute provides the list of words in the form of a sentence to the search engine. So if someone searches for one of the keywords listed by you in the META tag, then your web site would also appear in the result of the search. It is useful to include META tags that include as many keywords as possible. This makes the web page more likely to show up in a search.
You can also specify keywords by separating them by commas as illustrated in the following code fragment of Figure
<META NAME= "keywords" CONTENT= "Website, different courses offered, IGNOU ,mca, bca">
You can employ either of the methods of denoting the META tag as convenient.
Consider another example shown in Figure. This example demonstrates how to redirect a user if your site address has changed.
<HTML>
<HEAD>
<TITLE>IGNOU</TITLE>
<META HTTP-EQUIV="Refresh" CONTENT="5;URL=https://www.ignou.ac.in">
</HEAD>
<BODY>
<P>
Sorry! We have moved! The new URL is: www.ignou.ac.in
</p>
<p>
You will be redirected to new address in five seconds.
</p>
</BODY>
</HTML>
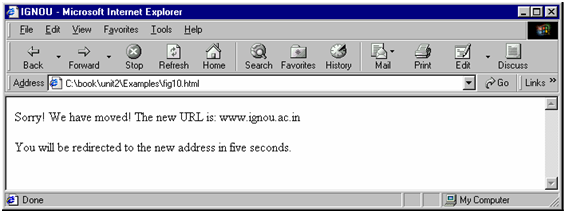
Figure: Redirecting a User if the Site has Moved