Memory Segmentation :
The memory in an 8086/8088 based system is organized as segmented memory. In this scheme, the whole physically available memory can be divided into a number of logical segments. Each segment is64K bytes in size and is addressed by 1 of the segment registers. The 16-bit contents of the segment register in fact point to the beginning location of a specific segment. To address a particular memory location within a segment, we need an offset address. The offset address is also 16-bit long so that the maximum offset value can be FFFFH, and thus the maximum size of segment is 64K locations.
To emphasize this segmented memory concept, we will take an example of a housing colony containing say, 100 houses. The easy method of numbering the houses will be just to assign the numbers from 1 to 100 to each house sequentially. Imagine, now, if 1 wants to find out house number 67, then he will begin from house number 1 and go on till he search the house, numbered 67. Consider another case where the 100 houses are arranged in the 10 x 10 (rows x columns) pattern. In this case, to search house number 67, 1 will directly go to the 6th row and then to the 7th column. In the second scheme, the efforts required for searching the similar house will be too less. This second scheme in our example is analogous to the segmented memory scheme, where the addresses are specified in terms of segment addresses analogous tooffset androws addresses analogous to columns.
The CPU 8086 is able to address 1Mbytes of physical memory. The complete1Mbytes memory may be divided into 16 segments, particular of 64Kbytes size. The addresses of the segments can be assigned as 0000H to F000H respectively. The offset address values are from 0000H to FFFFH so that the physical addresses range from 00000H to FFFFFH. In the above case, the segments are called non-overlapping segments. The non-overlapping segments are revealed in given figure (a).However, in some cases, the segments can be overlapping. Imagine a segment begins at a specific address and its maximum size may be 64Kbytes. But, if another segment begins before these 64Kbytes locations of the first segment, the 2 segments are said to be overlapping segments. The region of memory from the start of the second segment to the possible end of the first segment is known as overlapped segment area. Figure tells the phenomenon more clearly. The locations in the overlapped area can be addressed by the similar physical address generated from 2 different sets of segment and offset addresses. The major advantages of the segmented memory scheme are as follows:
1) Allows the memory capacity to be 1Mbytes although the actual addresses to be handled are of 16-bit size.
2) Let the placing of code, data and stack portions of the same program in different parts (segments) of memory, for data and code protection both.
3) Permits a program and/or its data to be put into different areas of memory eachtime program is executed, for instance provision for relocation may be done.
Inoverlapped Area Locations Physical Address = IF+ Cs = IF + CS + denoted the process of physical address formation.
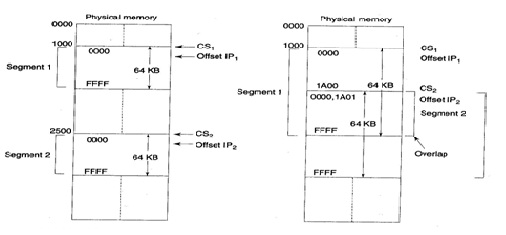
Fig: Non-overlapping Segments Fig: overlapping segment