Find out all the numbers c that satisfy the conclusions of the Mean Value Theorem for the given function.
f ( x ) = x3 + 2 x2 - x on [-1, 2]
Solution : There isn't in fact a lot to this problem other than to notice as well that since f (x) is a polynomial it is continuous and differentiable both (that means the derivative exists) on the interval given. Firstly let's find out the derivative.
f ′ ( x ) = 3x2 + 4x -1
Now, to determine the numbers which satisfy the conclusions of the Mean Value Theorem all we have to do is plug this into the formula specified by the Mean Value Theorem.
f ′ (c ) = f ( 2) - f ( -1) /2 - ( -1)
3c2 + 4c -1 = 14 - 2/3 = 12/3 = 4
Now, it is just a quadratic equation,
3c2 + 4c -1 = 4
3c2 + 4c - 5 = 0
By using the quadratic formula on this we obtain,
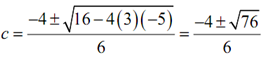
Thus, solving out gives two values of c.
c =( -4 +√76) /6 = 0.7863 c =( -4 +√76) /6 = -2.1196
Notice as well that only one of these is in fact in the interval given in the problem. That means we will exclude the second one (As it isn't in the interval). The number which we're after in this problem is c = 0.7863
Be careful to not suppose that just one of the numbers will work. This is possible for both of them to work.
Facts using the Mean Value Theorem
In both of these facts we are supposing the functions are continuous & differentiable on the interval [a,b].
Fact 1
If f ′ ( x ) = 0 for all x in an interval ( a, b ) then f ( x ) is constant on ( a, b ) .
This fact is extremely easy to prove so let's do that here. Take any two x's within the interval ( a, b ) , say x1 and x2 . Then since f ( x )is continuous & differential on [a,b] it has to also be continuous & differentiable on [ x1 , x2 ] . It means that we can apply the Mean Value Theorem for these two values of x. Doing this we get,
f ( x2 ) - f ( x1 ) = f ′ (c ) ( x2 - x1 )
Where x1 < c < x2 . But by supposition f ′ ( x ) = 0 for all x in an interval ( a, b ) and therefore in specific we must have,
f ′ (c ) = 0
Putting this in the equation above gives,
f ( x2 ) - f ( x1 ) = 0 ⇒ f ( x2 ) = f ( x1 )
Now, since x1 and x2 where any two values of x in the interval ( a, b ) we can illustrates that we ought to have f ( x2 ) = f ( x1 ) for all x1 and x2 in the interval and it is exactly what it means for a function to be a constant on the interval and thus we've proven the fact.
Fact 2
If f ′ ( x ) = g′ ( x ) for all x in an interval (a, b ) then in this interval we have f ( x ) =g ( x ) + c where c refer to some constant.
This fact is direct result of the fact1 and it is also easy to prove. If we first define,
h ( x ) = f ( x ) - g ( x )
Then since both f (x) & g (x) are continuous & differentiable in the interval ( a, b ) then so have to be h ( x ) . Thus the derivative of h ( x ) is,
h′ ( x ) = f ′ ( x ) - g ′ ( x )
Though, by supposition f ′ (x) = g ′ (x) for all x in an interval ( a, b ) and therefore we ought to have that h′ ( x ) = 0 for all x in an interval ( a, b ) . Thus, by Fact 1 h ( x ) has to be constant on the interval.
It means that we have,
h ( x ) = c
f ( x ) - g ( x ) = c
f ( x ) +g ( x ) = c
Which is what we were attempting to show.