Magnetic permeability and the B/H curve
To measure the relationship between field strength H and flux density B for a material, a sample is made into a closed ring and a magnetising coil wound onto it. Current flowing in this coil creates a m.m.f. equal to NI which in turn produces a magnetic field
H= NI/L
in the ring. So H is proportional to the current in the energising coil and may be obtained from direct measurement of I. If a change in the current occurs, the flux density changes and this will induce a transient 'back e.m.f' in a second coil that is also wound onto the ring.
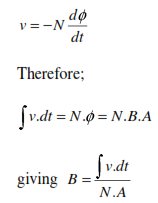
The integral of the back emf is proportional to B. Hence the relationship between B and H may be determined from measurement of I (to give H) and the induced back e.m.f in the coils (to give B).
The result of such measurements on various materials produces two types of curves - straight lines of low
B/H =µr
values and curves for which the value of B/H =µr varies. This first type are sub divided into paramagnetic
varies. This first type are sub divided into paramagnetic materials if B/H =µr >1 and diamagnetic if B/H =µr <1. The second type are ferromagnetic and have a more complicated dependence of B on H. At low H these have B/H =µr >>1 (typically 100 - 100000)

It is also found that ferromagnetic materials lose these high µr properties above a well-defined temperature (different for different materials) known as the Curie temperature. This typically r ranges from 200 - 750 °C and limits the maximum temperature that many electromagnetic devices can operate.
The temperature dependence of the ferromagnetic properties give a clue to the physical reason for the different
permeabilities of the materials. Diamagnetic and paramagnetic properties are attributable to the orbiting electrons within the atoms of the material. Ferromagnetic properties arise due to the orientation of atoms on a macroscopic scale so that the magnetic fields created by the orbiting electrons within each atom reinforce each other. These 'domains' of high magnetic strength may contain ~10-12 atoms each. The domains are initially randomly directed but under the influence of an external magnetic field, re-orientate to point in the same direction. Initially this is along the direction of the nearest crystal axis to the direction of the magnetic field.
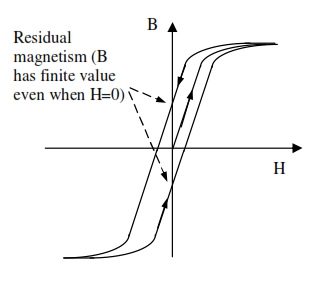
Steadily increasing the external field brings them directly into line with the external field direction.If the external field is now removed, the domains relax back to point in the nearest crystal direction, leaving a residual magnetism. Materials that have a strong residual magnetism are used for permanent magnets. Cycling the current over one complete cycle produces a hysteresis B/H curve