Magnetic force on a moving charge
Oersted also discovered that anytime a charge is moving in an area where a magnetic field exists, it experiences a force which is sometimes called the Hall Effect. This effect is one of the ways used to measure the strength of a magnetic field (by measuring the potential difference this can create). The magnitude of the force on a moving charge is given by
F = q v B
where F is the force on the charge in newtons, q is the charge in coulombs, v is the charge's velocity in m/s and B is the magnetic flux density in teslas.
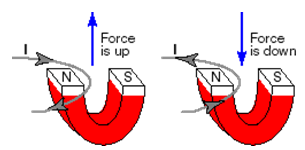
To determine the direction of the force on a moving charge, point the fingers of the right hand in the positive current direction with your palm facing the south pole of the magnetic field. Bend your fingers at 90o so that they are now pointing in the direction of the magnetic field and your thumb points in the direction of the force on the moving charge.
The force on the wire is given by
F = I L B
where F is the force in Newtons, I is the current in amps, L is the length of the wire in meters, and B is the magnetic flux density in teslas.
This means that any wire that carries current will generate its own magnetic field which can then exert a force on any other nearby wire which carries current.
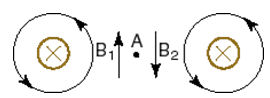
Example - Using the right hand rule, can you show that if you have two parallel wires carrying current in the same direction, the wires are pulled toward each other?
If we have two wires carrying current into the screen (indicated by x's, which stand for the tails of the positive current vectors), the magnetic field of the left hand wire will be clockwise around the wire - right thumb points into the paper and fingers of right hand curl clockwise. The other wire will also have a magnetic field clockwise around the wire. At point A halfway between the wires that means that B1 is B2 so that the wires will be pulled toward each other.
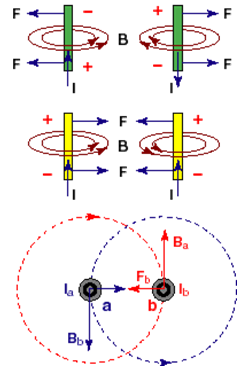
If the currents are in opposite directions the wires repel each other. Can you use the right hand rule to convince yourself of this?