Machine Coding the Programs
So far we have describe five programs which were written for hand coding by a programmer. In this, we will now have a deep look at how these programs may be translate to machine codes. In Appendix, the instruction set along with the Appendix is presented. This Appendix is self-explanatory to hand code mostly of the instructions. The V,S W, D, MOD, REG and R/M fields are appropriate decided depending upon the data types, addressing mode and the registers used. The table shows the details about how to select these fields.
Most of the instructions either have particular opcodes or they may be decided only by setting the V,S, W, D, REG, MOD and R/M fields suitably but the critical point is the calculation of jump addresses for intra segment branch instructions. Before beginning the coding of call or jump instructions, we will see some simpler coding examples.
Example :
MOV BL, CL
For hand coding this instruction, first we will have to note down the following features.
(i) It sets in the register/memory to/from register format.
(ii) It is an 8-bit operation.
(iii) BL is the destination register and CL is a source register.
Now from the feature (i) by using the Appendix, the op code format is given below.
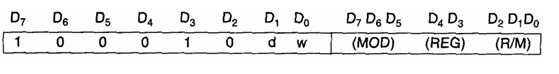
If d =1, then transformation of data is to the register shown by the REG field, for example the destination is a register (REG). If d = 0, the source is a register shown by the REG field. It is an 8-bit operation, therefore w bit is 0. If it had been a 16-bit operation, the w bit would have been 1.From referring to given table to search the REG to REG addressing in it, for example the last column with MOD 11. According to the Appendix when MOD is 11, the R/M field is treated as a REG field. The REG field which is used for source register and the R/M field are used for the destination register, if d is 0. If d =1, the REG field is utilized for destination and the R/M field is used to indicate source. the complete machine code of this instruction comes out to be now.
code dw MOD REG R/M
MOV BL, CL 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 001 0 1 1= 88 CB