In the long run, because of the assumption of free entry and exit of the firms, it's not possible for the firms to make super-normal profits nor it is possible for them to incur losses. Thereforebecause of the size of the industry decreasing or increasing in the long run, firms can only earn normal profits in this time duration.
Possibility of only normal profits can be elucidated as under.
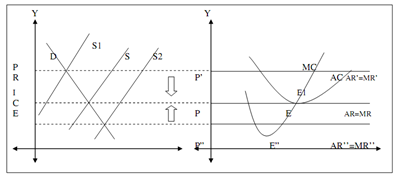
Figure: Long Run Equilibrium under Perfect Competition
Suppose that firm is earning a super-normal profit in the long run, because the industry's price (OP) (i.e. the firm's AR' = MR' = OP') is greater than its AC. In this condition, new firms would find this area of production to be attractive and therefore they would enter this industry in large numbers. With the number of firms increasing, supply in the industry also rises. As the supply rises, price will start lowering. This will go on till the supply curve becomes S1 to S. This results in fall in price from P' to P. Firm's AR=MR curve becomes tangential to the firms LAC at point E and so from the situation of earning super-normal profits the profit's size has been decreased to normal profit.
Suppose that firm is incurring losses in the long run because the industry's price (OP) (i.e. the firm's AR'' = MR'' = OP") is lower than its AC. In this situation, some of the firms which are unable to recover even their AVC will shut down and leave industry. With the number of firms decreasing, supply in the industry also falls. As the supply keeps falling, price will start rising. So price rises from P" to P. This will go on until the supply curve becomes S2 to S. Firm's AR=MR curve becomes tangential to the firms LAC and so from situation of incurring losses, firm's revenues have improved so as to convert losses into normal profits.
Therefore we can determine that in the long run, a firm under perfect Competition canonly earn normal profits but not earn super-normal profits or incur losses.