The Linked list is a chain of structures wherein each structure contains data in addition to pointer, which stores the address (link) of the next logical structure in the list.
A linked list is a data structure utilized to maintain a dynamic series of data. Think of linked list as a line of bogies of train where each of bogies is related on to the next bogie. If you have the idea of where the first bogie is, you can follow the link to the next bogie. By following links, you can determine any bogie of the train. While you get to a bogie which isn't holding (linked) on to another bogie, you know you are at the ending.
Linked lists work in the similar way, except programmers generally refer to nodes rather than bogies. A single node is described in the similar way as any other user defined type or the object, except that it also contains a pointer to a variable of the similar type as itself.
We will be seeing how the linked list is stored into the memory of the computer. In the following Figure, we can illustrates that start is a pointer i.e. pointing to the node that contains data as A& the node B is pointing to the node C and the last node is not pointing to any node. Given 1000,1050,1200 are memory addresses.
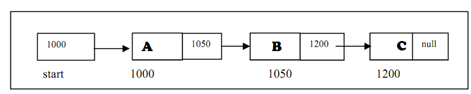
Figure: A Singly linked list
Consider the following definition:
typedefstruct node
{
int data;
struct node *next;
} list;
Once you consists a definition for list node, you can create a list easily by declaring a pointer to the first element, called as the "head". Generally a pointer is utilizedrather than a regular variable. List can be described as
list *head;
This is as simple as that! Now you have a linked list data structure. It isn't in general useful at the moment. You can illustrate if the list is empty. We will be seeing how to declare & define list-using pointers in the following program.
#include
typedefstruct node
{
int data;
struct node *next;
} list;
int main()
{
list *head = NULL; /* initialize list head to NULL */
if (head == NULL)
{
printf("The list is empty!\n");
}
}