Life in the Oceans:
Oceans are known as the largest and the thickest ecosystem. Tiny plants and animals exist in it, in immense numbers. A cubic meter of sea water may contain as many as 200,000 . organisms. Living forms occur, more or less, throughout the depth of the oceans, but they are more dense around the margins of continents and islands. The major factors that limit the quantity, and type of life in oceans are energy and nutrients. You have already studied that for all forms of life, energy is provided by sunlight either directly as in the case of plants, or indirectly to other forms of life ;ia the plants. In meadit waters, the intensity of light decreases rapidly with depth.
Even in the clearest and the purest water, there is hardly any light available at a depth of 200 metres, and photosynthesis cannot be sustained. Therefore, plants are only found in under water zones whex;e light is available. You must be wondering as to how do the plants keep themselves in the lighted zone? They have developed certain floating devices such as oil droplets in their cells or air filled sacs that help them to float in the upper layerspf water. These plants are of numerous kinds, some are tiny and microscopic, free floating and they drift with water whereas others are comparatively large and are fixed to the substratum. One of the factors governing their distribution, is the quality of light. We have just seen that sunlight penetrates to only a certain depth in water.
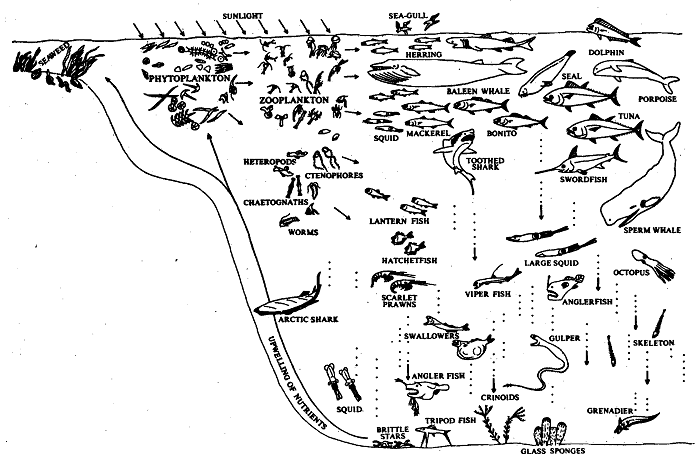
In the spectrum of colours which sunlight has, red is absorbed in the top layers of water, and then green; blue penetrates farthest. Naturally algae of complementary colours exist at various depths in water. Green is complementary to red, hence green algae predominates in the upper layers of water; similarly brown algae are a little deeper down, and red algae prevail in regions reached by blue light. What about the animal life? They too exhibit zonation, i.e., they are also distributed zone- wise. In the upper layers, small animals (zooplankton) co-exist with phytoplankton and derive energy from them.
A little below, the energy for animal life is obtained from wastes and dead bodies of organisms that sink, or from the living animals that swim down. The dead bodies that drift down from above, fall very slowly. For example, a small shrimp may take a week to reach 3000 metres. The rate of descent of organic matter, except for larger ones, is so slow that it is either consumed, decayed or dissolved before it reaches the deep waters or the bottom of the sea. Thus, as we go down in the ocean, the food becomes scarce. Beyond the depth of 200 metres or so, light does not penetrate and plants do not grow there. Hence the plant feeders have to be good swimmers, to get their food. Some of them come to the upper layers of water, take their food and go back. As you descend further, or below 600 metres, not only is sunlight absent but also the temperature drops, and the pressure increases. Here too. life exists. There are more than 2000 species of fish and other animals living at this depth. Let us see how these organisms have adapted to these difficult conditions.