Library Networks
A Library network is defined by Hunter and Bakewell as "A group of libraries and/or information service points, connected together for the purpose of satisfying specified requirements."
Wynar says that the term "network" has been used to describe multi-library organisations designed to facilitate inter-library loan, reference, duplicate exchange, processing and the like".
When any of the types of cooperation mentioned in Section 8.2 is to be achieved, networking of the libraries will be very useful. Through library networks cooperation and centralized processing becomes easy.
To give you an idea of networks and their services two illustrations are given below. Figure 1 is the network where each individual participating library gets the services from a central coordinating body of library.
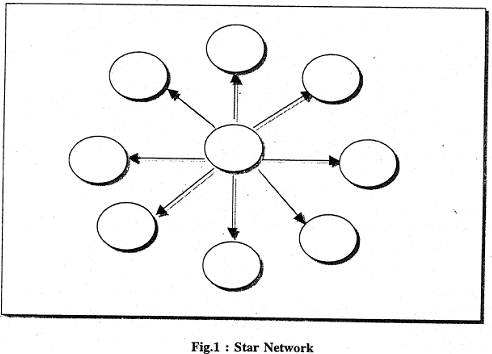
This type of network known as Star Network is illustrative of centralised processing and services.
Figure 2 illustrates the type of network where all participating libraries mutually exchange services. It is a network which illustrates of cooperative processing and services. It can also have multiple network paths as illustrated in Figure 3 and it is known as Mesh Network.
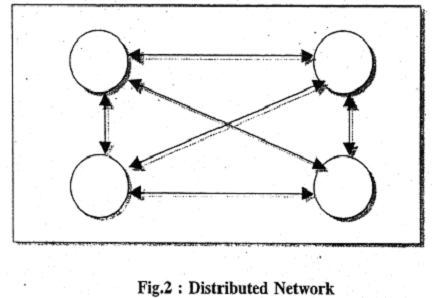
In Figure 2, arrows are indicated both ways. In other words, each one of the participating libraries will have access to each and every other library in the network.
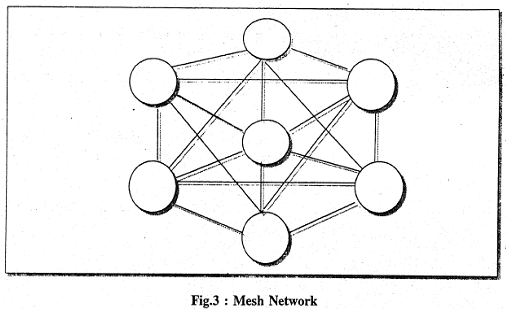
In a Mesh Network each centre known as node will inspect incoming messages or packets; accept those intended for it and pass on the others to appropriate nodes.
There can be other types of networks also which can help the libraries in their cooperative and centralized activities.
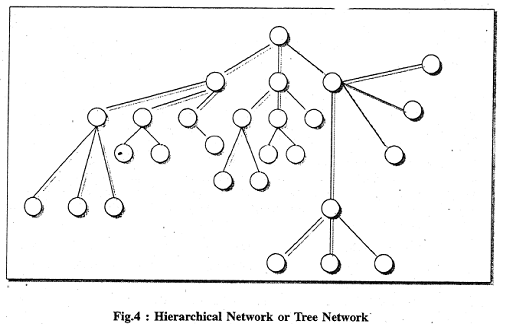
For example if the activities are confined to cenrtalized services like selection, acquisition, processing, information services, etc., within the same library system with several branches, a Hierarchical Network which is also known as Tree Network can be the solution.
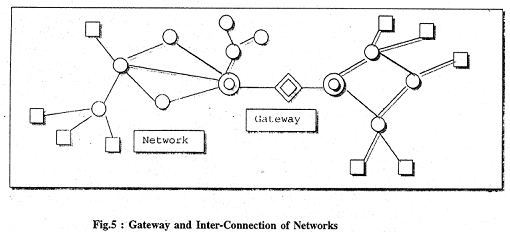
Two or more networks can be interconnected through what are known as 'Gateways'. A gateway, Purser says "is an interface between two distinct networks, in which some sort of conversion or mapping between the two formats and functions of data valid for each of the two networks takes place".
For example in our country Videsh Sanchar Nigam Limited (VSNL) acts as an international gateway. The illustration given below (figure 5) can give you some idea of a gateway and inter connection of networks.
In an attempt to serve the user better-by providing exact, pin-pointed and exhaustive information expeditiously, libraries and information centres are now-a=days taking advantage of the developments in information technology. Library networks world wide are playing a key role in this regard.