LIBRARY MANAGEMENT
The management of a library means, in simple terms, efficient and effective management of material (information resources), machinery, men and money to meet the objectives of the library. Accordingly, Unit 4 of this block deals with building, equipment and furniture for libraries followed $y two blocks (Blocks 2 & 3) dealing with the most important material, i.e., information resources. Managing men is dealt in Block 4 (Human Resource Development) and money in Block 5 (Library Finance and Budget).
From the discussion made so far about management theories, principles and procedures, it is obvious that they are very much relevant in managing libraries too. Yet it is very important for us to note that libraries are basically paternalistic, service-oriented and not-for-profit organisations. As a matter of fact, it is that part ' of management which is called "service management" which is more important to libraries than the management of industrial and profit-oriented organisations.
At this juncture, it is necessary for us to have a quick look at some of the basic characteristics of service and not-for-profit organisations. Four important characteristics of service are:
Intangibility (or impalpability): Services often may not directly appeal to the, senses of customers:
Inseparability (i.e., customer participation in service production) Service is usually produced' in the presence of customers and service production and consumption are inseparable.
Heterogeneity (variability): Service rendered cannot be fully standardised and as a result there will be variations in the quality of service rendered to different customers.
perishability (non-inventoriability): Many times service cannot be stored and an inventory developed for later physical distribution.
In addition to the above four of fundamental characteristics of service the following other characteristics of the service for not-for-profit organisations are worth noting. It is difficult to measure and compare performance of service organisations. It is equally difficult to inspect quality, determine and implement specifications, take samples and try in advance as well as determine the cost of a service.
Management of a library (as a service organisation) is accomplished by a combination of basic management functions and skills discussed earlier as well as management of roles. We can think of three important roles for a library manager (please note that roles do overlap with managerial functions):
- Interpersonal role: a) library manager as a figurehead with duties of a ceremonial nature, b) leading role, c) Raison role.
- Informational role: a) perpetually scanning and monitoring information: b) disseminator role, c) specific role of informing and satisfying various groups.
- Decisional role: a) As entrepreneur looking out for new ideas and adopt them for change b) solving unanticipated problems and handling disturbances, c) resources allocation role of dividing work and delegating authority, d) negotiator role.
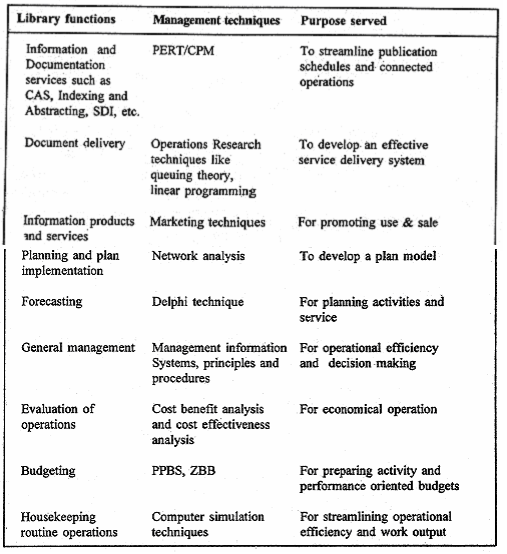
Libraries have grown with times in the social, cultural, scientific and technological environments in which they have been developing and operating. Modem libraries are not merely storehouses of knowledge and information but are also live and active institutions involved in a vital service to society. Today knowledge and information are considered as important as energy and biotechnology and hence have to be taken care of and managed well. Scientific management theories, principles and practices are, therefore, increasingly being applied to manage libraries to provide effective and quality service. In the light of what we have studied so far, some potential areas of library activities in which modem management techniques and methods could be applied are given below. The list is indicative and not exhaustive. The important point to note is that library managers and workers should develop an attitude and approach to scientific management and cultivate a culture so essential to proper library management. Table showing applications of management techniques to library functions The relationship between costs and benefits (i.e. inputs and output/outcome) is blurred. Output is often a mix of physical facilities and mental or physical labour. There is no title or ownership transfer when a service is rendered. Service organisations are labour (personality) and equipment intensive and are dominated by professionals. In service organisations, excellence is rare and mediocrity common and, surprisingly, dissatisfaction is rarely conveyed by customers. Service organisations are usually small and operate at a single location. Lastly, market forces play a less significant role in service organisations. The characteristics of service organisations are by no means exhaustive. But these are most basic and have their own impact on the nature and style of service management.
Table showing applications of management techniques to library functions