Krushkal's algorithm uses the concept of forest of trees. At first the forest contains n single node trees (and no edges). At each of the step, we add on one (the cheapest one) edge so that it links two trees together. If it makes a cycle, simply it would mean that it links two nodes that were connected already. So, we reject it.
The steps in Kruskal's Algorithm are as:
1. The forest is constructed through the graph G - along each node as a separate tree in the forest.
2. The edges are placed within a priority queue.
3. Do till we have added n-1 edges to the graph,
I. Extract the lowest cost edge from the queue.
II. If it makes a cycle, then a link already exists among the concerned nodes. So reject it.
III. Otherwise add it to the forest. Adding it to the forest will join two trees together.
The forest of trees is a division of the original set of nodes. At first all the trees have exactly one node in them. As the algorithm progresses, we make a union of two of the trees (sub-sets), until the partition has only one sub-set containing all the nodes eventually.
Let us see the sequence of operations to determine the Minimum Cost Spanning Tree(MST) in a graph via Kruskal's algorithm. Suppose the graph of graph shown in figure and below figure illustrates the construction of MST of graph of Figure
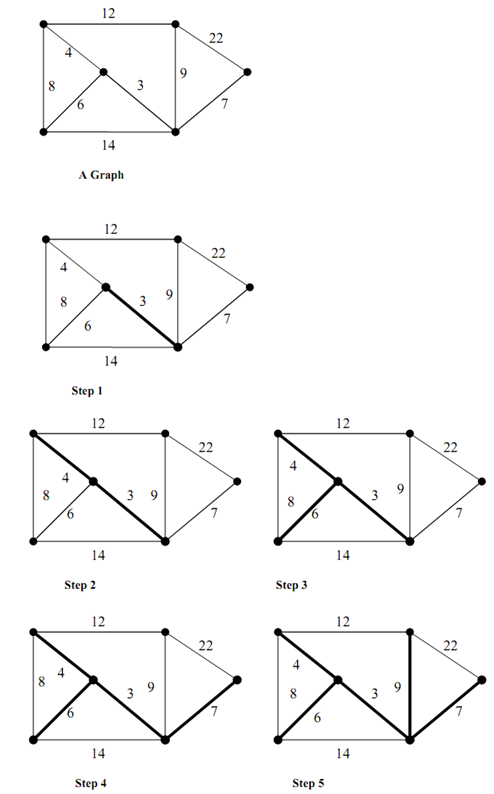
Figure: A Graph
Figure: Construction of Minimum Cost Spanning Tree for the Graph by application of Kruskal's algorithm
The following are several steps in the construction of MST for the graph of Figure via Kruskal's algorithm.
Step 1 : The lowest cost edge is chosen from the graph that is not in MST (initially MST is empty). The cheapest edge is 3 that is added to the MST (illustrated in bold edges)
Step 2: The next cheap edge which is not in MST is added (edge with cost 4).
Step 3 : The next lowest cost edge that is not in MST is added (edge with cost 6).
Step 4 : The next lowest cost edge that is not in MST is added (edge with cost 7).
Step 5 : The next lowest cost edge that is not in MST is 8 but form a cycle. Hence, it is discarded. The next lowest cost edge 9 is added. Now the MST has all the vertices of the graph. This results in the MST of the original graph.