KINEMATICS I
1. x(t) is called displacement and it denotes the position of the body at a particular time. If the displacement is positive then that body is to the right of the chosen origin and if negative, then it is to the left of the chosen origin.
2. If the body is moving with an average speed v then in the time t it will cover the distance d=vt.
But actually, the speed of a car changes from time to time and so one must limit the use of this formula to the small time differences only. So, more precisely, one defines an average speed over the small time interval is given as Δt:
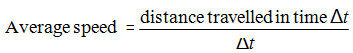
3. The instantaneous velocity at any time t is given as:
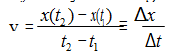
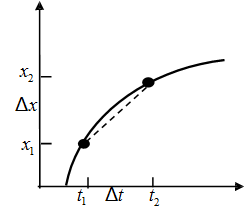
Where Δx and Δt are both very small quantities which tend to zero but their ratio v does not.
4. Similar to as we have defined velocity as the rate of change of distance, similarly we can define the instantaneous acceleration at any time t as:
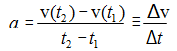
Where Δv and Δt are both very small quantities which tend to zero but their ratio a is not zero, in general. Negative acceleration is called the deceleration. The speed of the decelerating body decreases with the time.
5. Some students gets puzzled by the fact that the body can have a very large acceleration but can be standing still at a given interval of time. Indeed, it can be moving in opposite direction to its acceleration. There is actually nothing weird here because the velocity, position, and acceleration are independent quantities. This means that while specifying one we do not specify the other.
6. For constant speed and the body which is at point x=0 at time t=0, x rises linearly with the time t,
x ∝ t (or x = vt ).
If body is at the position x0 at time t = 0, then at time t, x = x0 + vt.
7. For the constant acceleration and a body that begins from rest at t = 0, v increases linearly with the time, v ∝ t (or v = at ). If the body has the speed of v0 at t = 0, then at time t, v = at + v0 .
8. We know above how far the body is moving at the constant speed moves in time period t. However what if the body is changing its speed constantly? If the speed is increasing linearly (that is constant acceleration), then the answer is particularly simple: just use the same formula as used in the above equation
(6) but use the average speed: (v0 + v0 + at) / 2 . So we get that 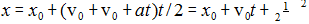 . This formula tells you that how far a body moves in time interval t if it moves with the constant acceleration a, and if starts at position x0 at t=0 with the speed of v0 .
. This formula tells you that how far a body moves in time interval t if it moves with the constant acceleration a, and if starts at position x0 at t=0 with the speed of v0 .
9. We can eradicate the time using (7) equation, and derive an another useful formula which tells us what the final speed will be after the body has travelled the distance equal to x - x0 after time t, v = v0 + 2a( x - x0 ).
10. Vectors, a quantity which has a size as well as direction is called a vector. So, for example, the wind blows with some speed and in some direction. So the wind velocity is a vector.
11. If we choose axes, then a vector is fixed by its components along those axes. In one dimension, a vector has only one component (call it the x-component). In two dimensions, a vector has both x and y components. In three dimensions, the components are along the x,y,z axes.
12. If we denote a vector G = ( x, y) then, r = x = r cosθ , and r = y = r sin θ .
Note that x2 + y 2 = r 2 . Also, that tan θ = y / x.
13. Addition of two vectors is possible geometrically. We take any one vector, move
it without changing its direction such that both the vectors initiate from the same point, and then form a parallelogram. The parallelogram's diagonal is the resultant.
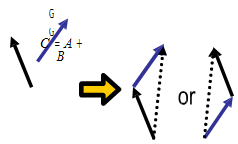
14. The two vectors can also be added by making use of algebra. In this case, we straight add the components of the two vectors along with each axis separately. So, for instance,
The resultant vector when we put two vectors together as
(1.5, 2.4) + (1, -1) = (2.5,1.4).