IPv6 packet Format
The format of an IPv6 header is shown in figure. Although IPv6 addresses are four times the size of IPv4 address the basic IPv6 header is only twice the size of an Ipv4 header thus decreasing the impact of the larger address fields. The files of the IPv6 header are:
Version : This represents the IP version number. This fields value is 6 for IPv6 and 4 for IPv4. This field is in the same location as the version fields in the IPv6 header making it simple for an IP node to quickly distinguish an IPv4 packet from an IPv6 packet.
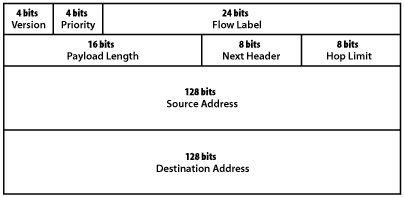
Figure IPv6 packet format
Priority : This enables a source to identity the desired delivery priority of the packet .
Flow label: This is used by a source to identify associated packet needing the same type of special handling. Such as a real time service between a pair of hosts .
Payload length: This is the length of the portion of the packet following the header in octets. The maximum value in this field is 65.535 if this field contains zero it means that the packet contains a payload larger than 64 K bytes and the actual payload length value is carried in a jumbo payload hop by hop option.
Next heard : This identifies the type of header immediately followings the eIPv6 header and uses the same values as the IPv4 protocol fields where applicable. The next header fields can indicate an options header higher layer protocols or no protocols above IP.
Hop limit: This specifies the maximum number of hops that a packet may take before it is discarded. This value is set by the source and decremented by one by each node that forwards the packet the packet is discarded if the hop limit reaches zero. The comparable field in IPv4 is the TTL field it was renamed for IPv6 because the value limits the number hops, not the amount of time that a packet can stay in the network.
Source address :This is the IPv6 address of the originator of the packet.
Destination address: This is the IPv6 address of the intended recipients of the packet.