Internet Service Provider (ISP)
This supper fast network spanning the world from one major metropolitan area to another is provided by a handful of national internet service providers (ISPs). These organizations connections running at approximately 45Mbps linked up at specified interconnection points called national access points ( which are located in major metropolitan areas). Local ISPs connect to this backbone through routers so that data can be carried through the backbone to its destination.
Each ISP is equipped with own contingency backbone network or is at least equipped with an outsourced backup. These smaller networks are interlinked and intertwined to provide the multi faceted backup redundancy needed to keep the web intact in case of partial failure through peering and transit agreements.
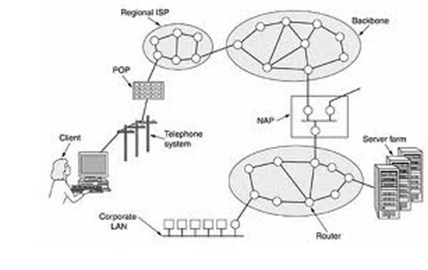
Overview of the internet
Let us assume that a client calls his or herI SP ( Internet Service Provider ) over a dialup telephone line as shown in figure 2.18. the modem within the PC that converts the digital signals. The computer processes to analog signals that can pass unhindered over the telephone systems. These signals are transferred to the ISP POP (Point of Presences) where they are removed from the telephone systems and get entered into the ISP regional networks. From this point the systems is fully digital and packet switched.
The ISP regional networks consists of interconnected routers in the various cities the ISP serves. If the packet is destined for a host served directly by the ISP the packet will delivered to the host. Otherwise it is handed over the ISP backbone operator.
The major backbone operator companies like AT & T and sprint operate will large international backbone networks with thousands of routers connected by high and bandwidth fiber optics. Large corporations and hosting services that run server farms( Machines that can serve thousands of web pages per second) often connect directly to the backbone. Backbone operators encourage this direct connection by renting space which are called as carrier hotels, basically equipment racks in the same room as the router to allow short fast connections between server forms and the backbone.
If a packet given to the backbone is destined for ands ISP company served by the backbone, the packet is sent to the closest router and handed off there. However many backbone of varying sizes, exist in the world so a packet may have to go to a competing connects at the NAPs. Basically a NAP is a room full of routers at least one per backbone. A LAN in the room connect all the routers so packets can be forwarded from any backbone to nay other backbone. In addition to being interconnected at NAPs the large backbones have numerous direct connections between their routers. This techniques is known as private peering.