Interconnection Network
Introduction
This unit discusses the types and properties of interconnection networks. In multiprocessor systems, there are multiple I/O modules, multiple processing elements and multiple memory modules. Each processor can access any of the I/O units and any of the memory modules. The connectivity among these is performed by interconnection networks.
Therefore, an interconnection network is used for swap data between two processors in a multistage network. Memory bottleneck is a basic limitation of Von Newman architecture. In this case of multiprocessor systems, the performance will be brutally affected in case the data exchange between processors is late. The multiprocessor system has single global shared memory and every processor has a small local memory. The processors can access data from memory associated with another processor or from shared memory using an interconnection network. Thus, interconnection networks play a essential role in determining the general performance of the multiprocessor systems. The interconnection networks are similar to customary network systems consisting of edges and nodes. The nodes are switches having some input and some output (say n input and m output) lines. Depending on the switch connection, the data is promoted from input lines to output lines. The interconnection network is placed among various devices in the multiprocessor network.
The architecture of a general multiprocessor is detremined in Figure 1. In the multiprocessor systems, these are multiple processor modules (each processor module consists of a processing element, small sized local memory and cache memory ), shared peripheral devices and shared global memory.
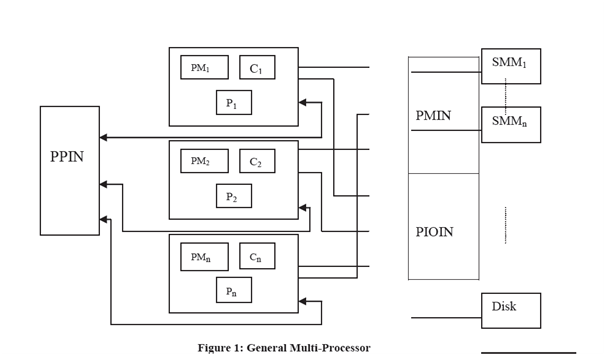
PIOIN= Processor to I/O Interconnection Network
PMIN = Processor to Memory Interconnection Network
PM = Processor Module
PPIN = Processor to Processor Interconnection Network
Module communicates with diffrent modules peripheral devices and shared memory using interconnection networks.