Inflation-Unemployment Trade-off under Rational Expectations:
Robert Lucas (1972) pointed out another implication of the above hypothesis of adaptive expectations. Suppose in a particular period (say period 0) the unemployment rate is lower than the natural rate. Then Φ(0), the actual rate of inflation in period 0 must have been greater than Φe(0), the rate of inflation expected by workers. Now suppose that the rate of growth of nominal demand is such that over time there is a constant rate of inflation Φ(0). Then, from (5.5) it follows that for all t≥0,
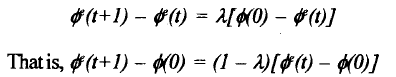
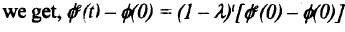
That is, if the expected rate of inflation is less than the actual rate of inflation in mod 0 it will continue to be so in all future time periods even though the difference between the two rates converges to 0 as t->∞.
The implication is that together with a constant rate of inflation, the economy can have a rising rate of unemployment (because the difference between the actual rate of inflation and the rate of inflation expected by workers diminishes over time) but the rate of unemployment can still be lower than the natural rate in every time period (because the actual rate of inflation is always greater than the rate expected by workers). That is over the long run, together with a constant rate of inflation, the economy could still have an average rate of unemployment lower than the natural rate.
Moreover, the above solution also implies that ceteris paribus the greater the value of Φ(0), the greater would be the derivation the actual from the expected rate of inflation in any time period. Therefore, the greater would be the deviation of the actual rate of unemployment from the natural rate in any time period. Hence, the higher the constant rate of inflation in the economy, the lower would be the long-run average rate of unemployment.
This implies that while macroeconomic policy cannot achieve a constant and permanently lower rate of unemployment in an anomy by choosing a constant but permanently higher rate of Won, an inflation-unemployment trade-off still exists. By choosing a constant but permanently higher rate of inflation policy makers can still -achieve a permanently lower rate of unemployment in each period resulting in a lower long-run average rate of unemployment.