Individual Demand
* The Individual Demand Curve
- Two significant Properties of Demand Curves
- 1) The level of utility which can be attained changes while moving along the curve.
- 2) At every instant on demand curve, the consumer is maximizing utility by fulfilling the condition that the MRS of food for clothing equals the ratio of prices of food and clothing.
Effect of Price Change
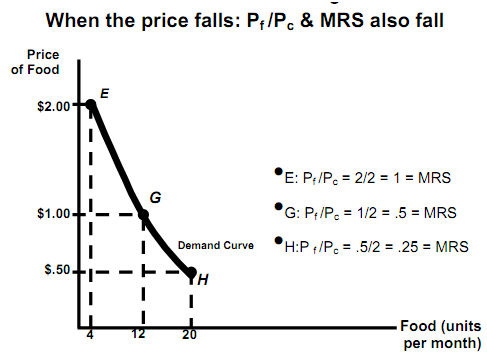
Individual Demand
* Income Changes
- Using figures developed earlier, the impact of a change in income can be illustrated by using indifference curves.
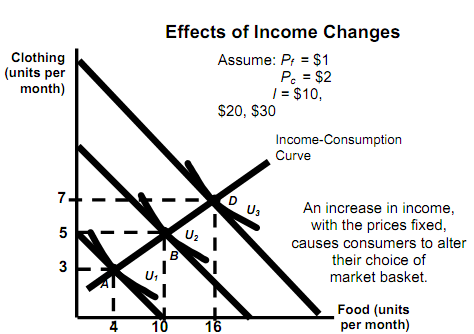
Effects of Income Changes
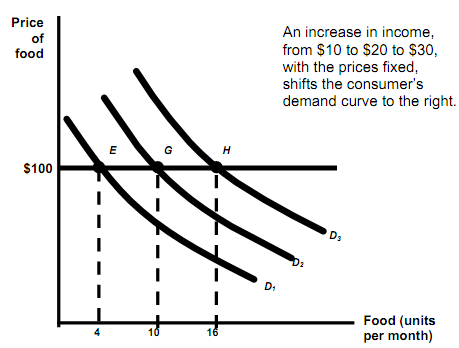
- The income-consumption curve traces out utility maximizing combinations of food and clothing linked with every income level.
- An increase in income shifts budget line to right, increasing consumption along income-consumption curve.
- At the same time, increase in income shifts demand curve to right.
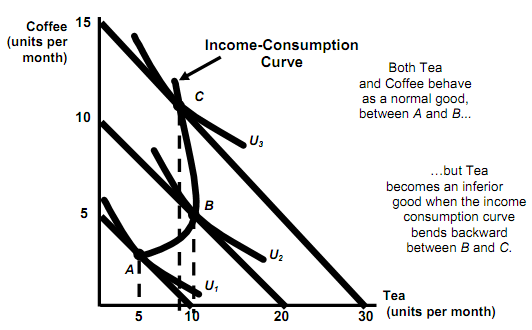
* Normal Good vs. Inferior Good
- Income Changes
- When income and consumption curve is having positive slope:
-The quantity demanded increases with the increase income.
-The income elasticity of demand is positive in nature.
-The product is a normal good.
- When income consumption curve is having negative slope:
-The quantity demanded decreases with the increase in income.
-The income elasticity of demand is negative in nature.
-This good is an inferior good.
An Inferior Good